基于壳聚糖衍生物的新型抗菌剂的制备与性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-22 19:35:49
摘 要
在日常生活中,人们常常面临着细菌感染的问题。抗生素的发明,在一定程度上缓解了细菌对人们的危害。但是抗生素的过量使用,会使抗生素对细菌失效,对人们生活造成了严重的危害。由此人们发明了许多新的抗菌纳米粒子,许多抗菌纳米粒子具有很好的杀菌功能以及防止细菌产生耐药性,但同时大部分抗菌纳米粒子的生物相容性不高,不适合在人体内使用。为消灭各类对人体有害的细菌,同时又满足人们对于健康的新要求,开发生物相容高的抗菌材料刻不容缓。
在本文中,我利用一种简单的静电自组装法,通过壳聚糖硫酸酯上面的硫酸根离子和壳聚糖上面的铵根离子生成壳聚糖/壳聚糖硫酸酯纳米粒子,然后将纳米银包裹在其中,分析其理化性能,评价其生物相容性和抗菌性能。具体研究过程如下:
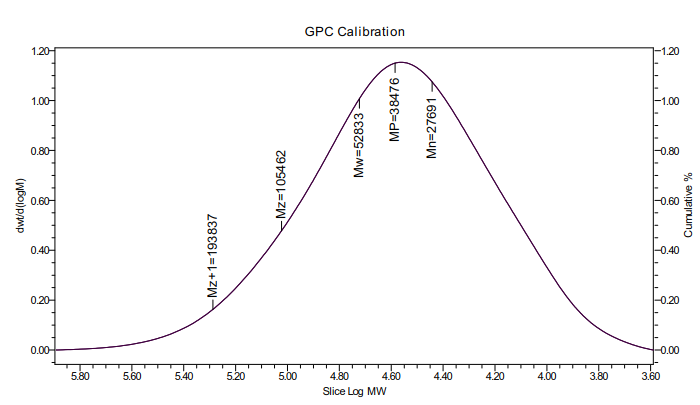
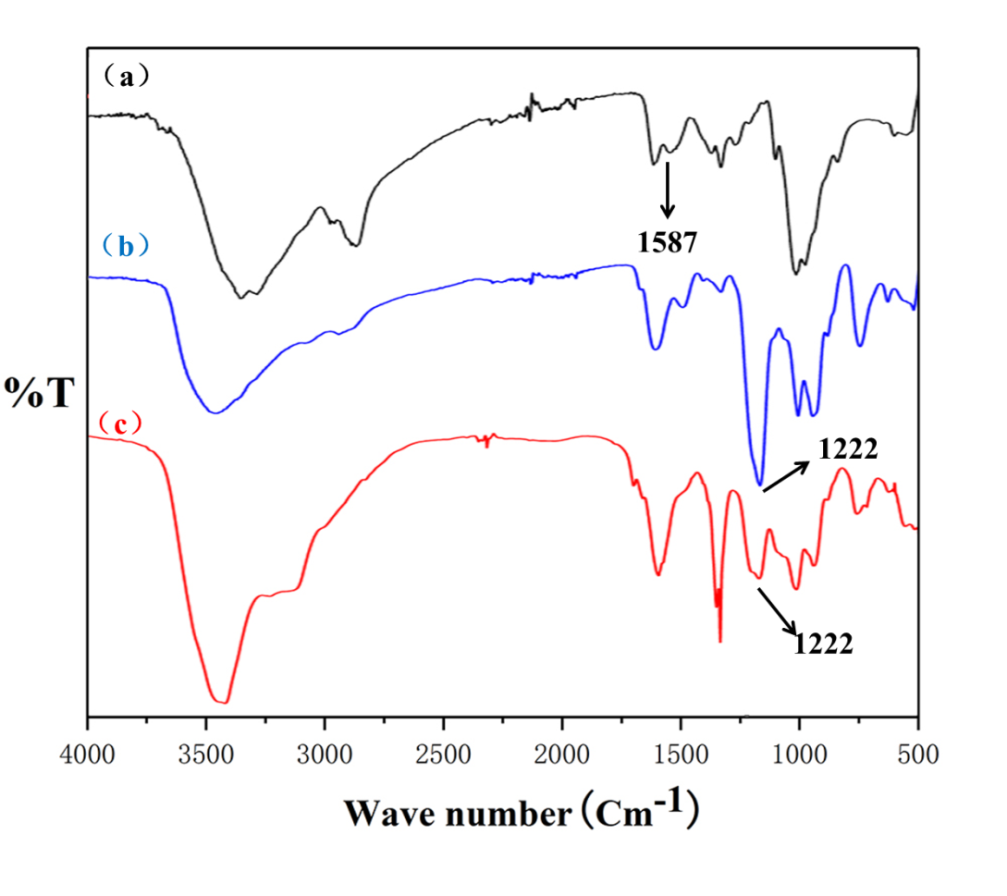
(1):以壳聚糖为原料,通过均相反应合成壳聚糖硫酸酯。通过傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR)、元素分析、水相凝胶色谱仪。对壳聚糖硫酸酯结构、硫酸酯基接枝率、壳聚糖硫酸酯的分子量进行表征。
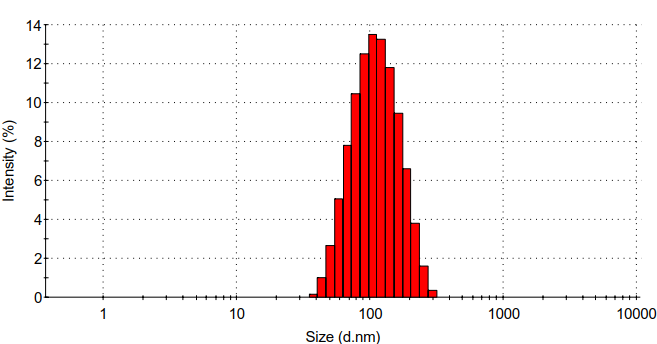
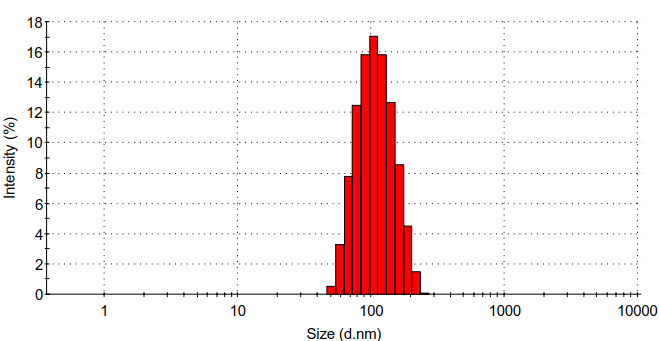
(2) :通过静电自组装法合成壳聚糖/壳聚糖硫酸酯聚电解质纳米凝胶。利用马尔文的Zeta电位检测、马尔文的DLS、赛默飞的FT-IR、日本电子公司的TEM对壳聚糖/壳聚糖硫酸酯聚电解质纳米凝胶的表面电位、水合粒径、化学结构、形貌进行表征。发现壳聚糖/壳聚糖硫酸酯聚电解质纳米凝胶水合粒径为95.8 nm,PDI为0.192,Zeta电位为-25 mv。
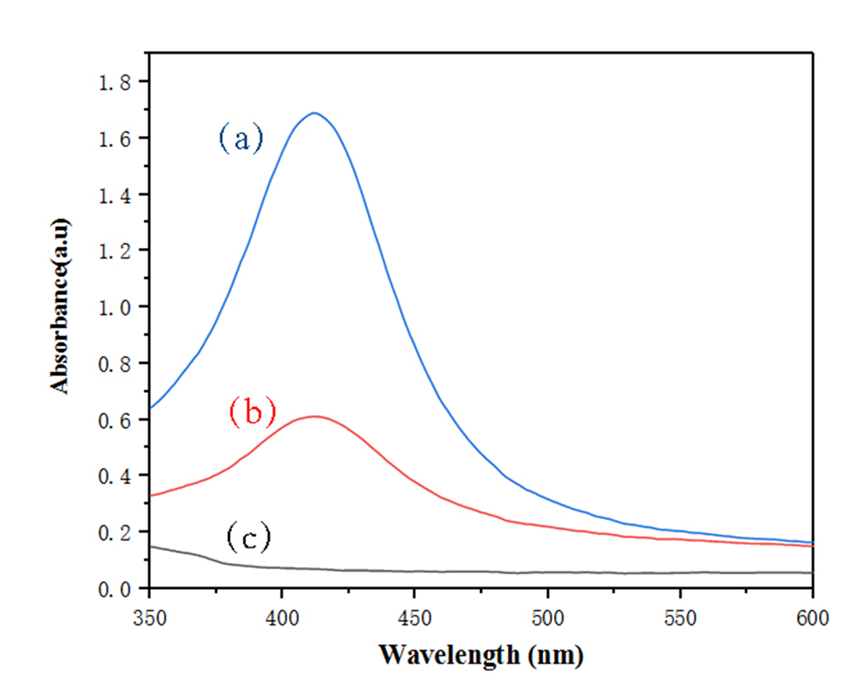
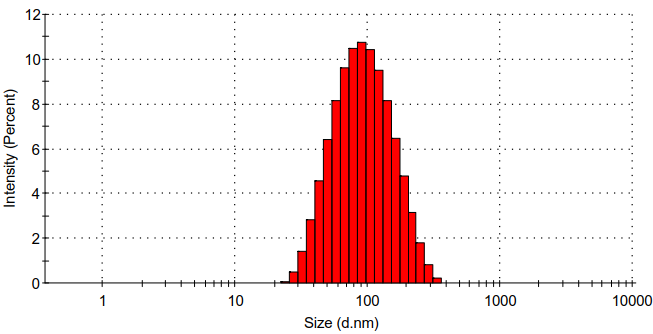
(3):以NaBH4为还原剂,将银离子变为纳米银,得到负载纳米银的壳聚糖/壳聚糖硫酸酯聚电解质纳米凝胶。利用Zeta电位检测、DLS、TEM、UV-vis、ICP对负载纳米银的壳聚糖/壳聚糖硫酸酯聚电解质纳米凝胶的表面电位、水合粒径、纳米银生成情况、纳米银负载量、形貌进行表征,证明成功合成了负载纳米银的壳聚糖/壳聚糖硫酸酯聚电解质纳米凝胶。
(4):利用CCK-8探针测试壳聚糖/壳聚糖硫酸酯聚电解质纳米凝胶、负载纳米银含量不同的壳聚糖/壳聚糖硫酸酯聚电解质纳米凝胶对小鼠成纤维细胞(L929)的细胞毒性,评价纳米凝胶的生物相容性。发现负载纳米银含量为
5.7 μg/mL的纳米凝胶生物相容性很好,为进一步拓展应用奠下基础。
(5):以金黄葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌为代表菌种,利用平板涂布法、场发射扫描电镜(FESEM)、活死菌染色法来评价其纳米凝胶的抗菌性能。发现负载纳米银含量为5.7 μg/mL的纳米凝胶能在90 min时杀死99%的大肠杆菌和99.9%的金黄葡萄球菌。
关键词:抗菌 聚电解质复合物 壳聚糖 壳聚糖硫酸酯 纳米银 生物相容性
Preparation and properties of novel antimicrobial agents based on chitosan derivatives
Abstract
In daily life, people often face the problem of bacterial infection. However, excessive use of antibiotics can cause bacteria to develop drug resistance, and produce superbugs such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, which cause serious harm to people's lives. Therefore, many new antibacterial nanoparticles have been invented. Many antibacterial nanoparticles have good bactericidal function and prevent bacteria from developing drug resistance. In order to eliminate all kinds of harmful bacteria and meet people's new requirements for health, it is urgent to develop biocompatible and high antimicrobial materials.
In this paper, a simple electrostatic self-assembly method was used to synthesize chitosan/chitosan sulfate polyelectrolyte nanogels by electrostatic attraction between sulfate ions on chitosan sulfate and ammonium ions on chitosan sulfate. Then chitosan/chitosan sulfate polyelectrolyte nanogels were used as templates and sodium borohydride was used as reducing agent to reduce silver ions in situ to obtain chitosan/chitosan sulfate polyelectrolyte nanogels loaded with silver nanoparticles. The specific research process is as follows:
(1): Chitosan sulfate was synthesized from chitosan by homogeneous reaction. Through Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), elemental analysis, GPC. It can be proved that the chitosan sulfuric acid ester with 3, 6-o-chitosan sulfuric acid ester as the main component is synthesized, in which the graft rate of sulfuric acid ester group is 29%, and the viscosity average molecular weight of chitosan sulfuric acid ester is 38476Da.
(2): Chitosan/chitosan sulfate polyelectrolyte nanogels was synthesized by electrostatic self-assembly method. Surface potential, hydrated particle size, chemical structure and morphology of chitosan/chitosan sulfate polyelectrolyte nanogels were characterized by Zeta potential detection, dynamic light scattering particle size analysis (DLS), Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and transmission electron microscope (TEM).It was found that the particle size of chitosan/chitosan sulfate polyelectrolyte nanogels was 95.8 nm,PDI was 0.192, and Zeta potential was -25 mv.
(3) :Sodium borohydride was used as the reducing agent to reduce silver ions to nanosilver in situ, and chitosan/chitosan sulfate polyelectrolyte nanogels loaded with nanosilver was obtained. Use Zeta potential detection, dynamic light scattering (DLS) for particle size analysis, transmission electron microscope (TEM), ultraviolet-visible absorption spectra (UV-vis), inductively coupled plasma spectrometer (ICP) of nanosilver chitosan/chitosan sulfate polyelectrolyte surface potential of nanogels, hydrated, nanosilver particle size generate situation, load, silver nanoparticles morphology characterization, proved the successful synthesis of nanosilver chitosan/chitosan sulfate polyelectrolyte nanogels.
(4) : cck-8 probe was used to test the cytotoxicity of chitosan/chitosan sulfate polyelectrolyte nanogels and chitosan/chitosan sulfate polyelectrolyte nanogels loaded with different silver contents on mouse macrophages (RAW). The biocompatibility of nanogels loaded with 5.7 μg/ml of silver was found to be excellent.
(5) : staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli were used as representative strains to evaluate the antimicrobial performance of the nanogels by plate coating method, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and live dead bacteria staining. It was found that the nanogels loaded with 5.7 μg/ml nanogels could kill 99% of e. coli and 99.9% of staphylococcus aureus at 90 min.
Key Words: Antibacterial materials ; Nano Hydrogels ; Chitosan ; Nanosilver
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract III
第一章 导论 1
1.1抗菌材料以及面临的问题 1
1.2壳聚糖 1
1.3壳聚糖硫酸酯 1
1.4纳米银 2
1.4.1纳米银抗菌机理 2
1.4.2纳米银安全性问题 2
1.5聚电解质纳米凝胶 3
1.6课题选题意义 3
1.7研究内容 3
第二章 壳聚糖硫酸酯的制备 5
2.1实验试剂 5
2.2实验仪器 5
2.3壳聚糖硫酸酯的合成 5
2.4结果与讨论 6
2.4.1壳聚糖硫酸酯傅里叶红外光谱表征 6
2.4.2SCS元素分析 6
2.4.3壳聚糖硫酸酯粘均分子量测试 7
第三章 壳聚糖硫酸酯纳米凝胶的制备 8
3.1实验试剂 8
3.2实验仪器 8
3.3壳聚糖硫酸酯纳米凝胶的制备 8
3.4负载纳米银的壳聚糖硫酸酯纳米凝胶的制备 8
3.5 CS/SCS纳米凝胶和载CS/SCS@Ag纳米凝胶的表征 9
3.5.1 CS/SCS纳米凝胶FT-IR 9
3.5.2 紫外可见光谱分析 9
3.5.3 CS/SCS@Ag纳米凝胶元素分析 10
3.5.4 水合粒径分析 10
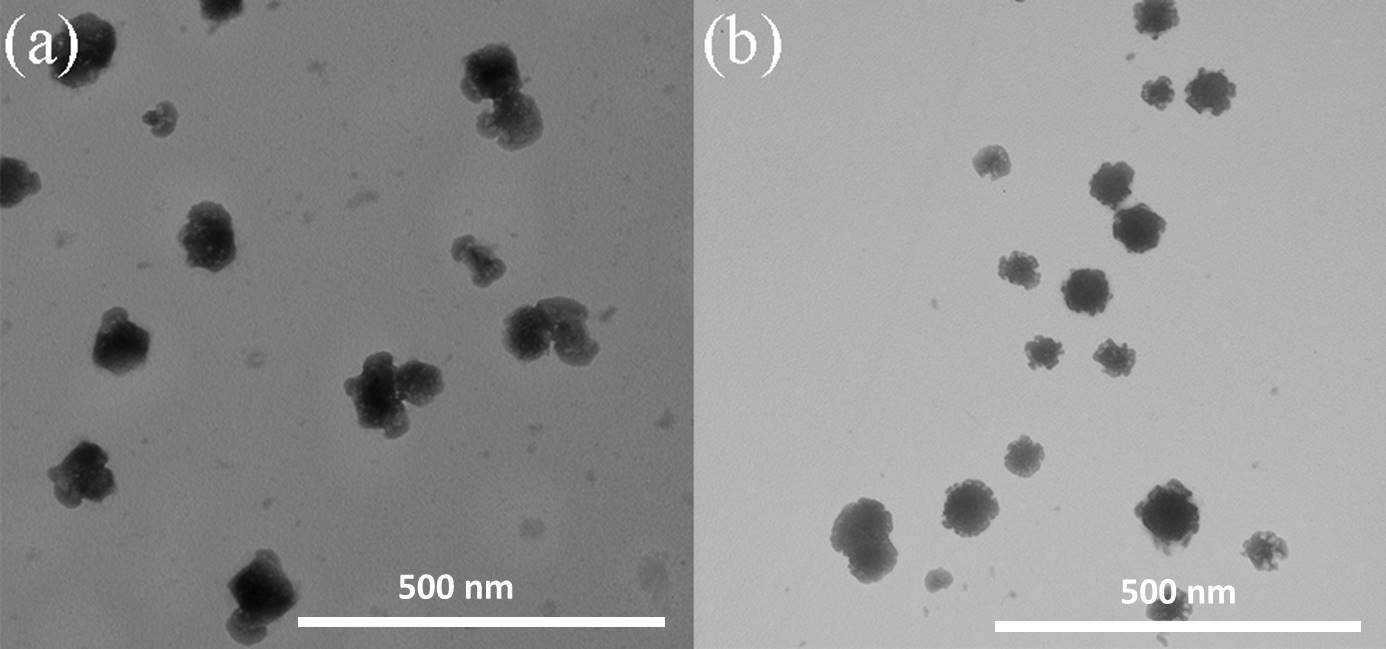
3.5.5 形貌表征 12
3.5.6 Zeta电位 13
第四章 “细胞毒性实验 14
4.1 细胞毒性实验部分 14
4.1.1 实验试剂 14
4.1.2 实验仪器 14
4.1.3 实验细胞 14
4.1.4 完全培养基配制 14
4.1.5 细胞复苏 14
4.1.6 接种细胞 15
4.1.7 纳米凝胶和细胞共孵育 15
4.1.8 细胞毒性检测 15
4.2 结果与讨论 15
4.2.1 细胞毒性分析 15
第五章 抗菌性能研究 18
5.1 实验准备 18
5.1.1 实验试剂 18
5.1.2 实验仪器 18
5.1.3 实验菌种 18
5.1.4 LB液体培养基配制 18
5.1.5 LB固体培养基配制 18
5.1.6 平板培养基制备 18
5.1.7 无菌生理盐水配置 18
5.1.8细菌扩大培养 19
5.1.9原菌液浓度确定 19
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



