分子筛膜用于二甲基乙酰胺渗透汽化脱水毕业论文
2020-04-22 19:38:42
摘 要
随着有机溶剂需求量的日益增加,溶剂的回收与提纯显得尤为关键。传统有机溶剂脱水方法如精馏、吸附等存在工艺流程复杂、分离效率低、能耗高、二次污染等问题。而渗透汽化是一种高效节能的膜分离技术,不受气液平衡限制,适用于共沸或近沸混合物的分离。分子筛膜具有均一的孔道结构、良好的热稳定性和耐溶剂性,在渗透汽化脱水分离中表现出高通量及高选择性。
本文主要考察渗透汽化操作条件对中空纤维NaA、DDR分子筛膜分离性能的影响以及在二甲基乙酰胺/水体系中渗透汽化稳定性。
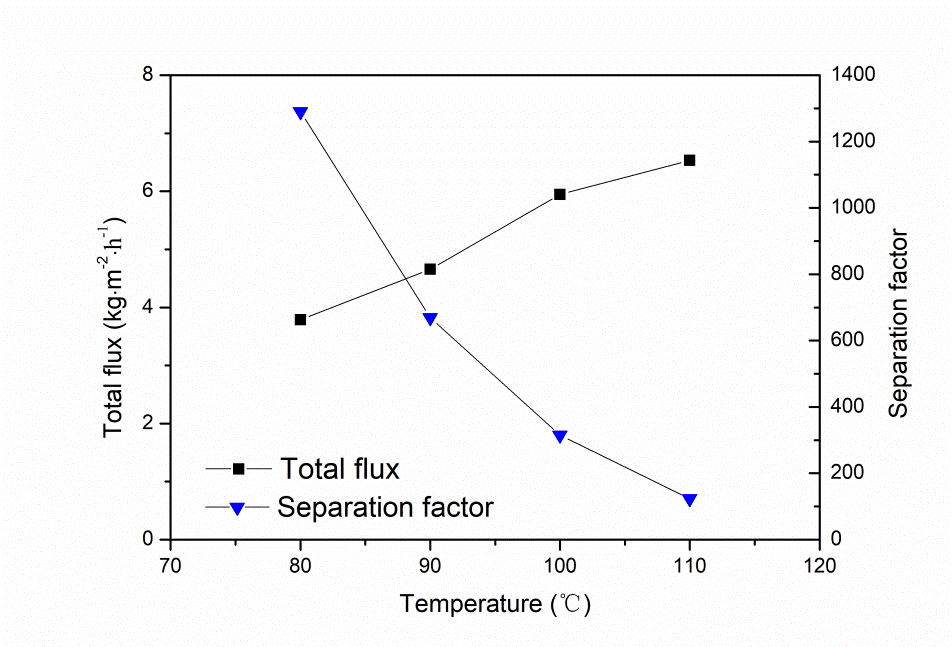
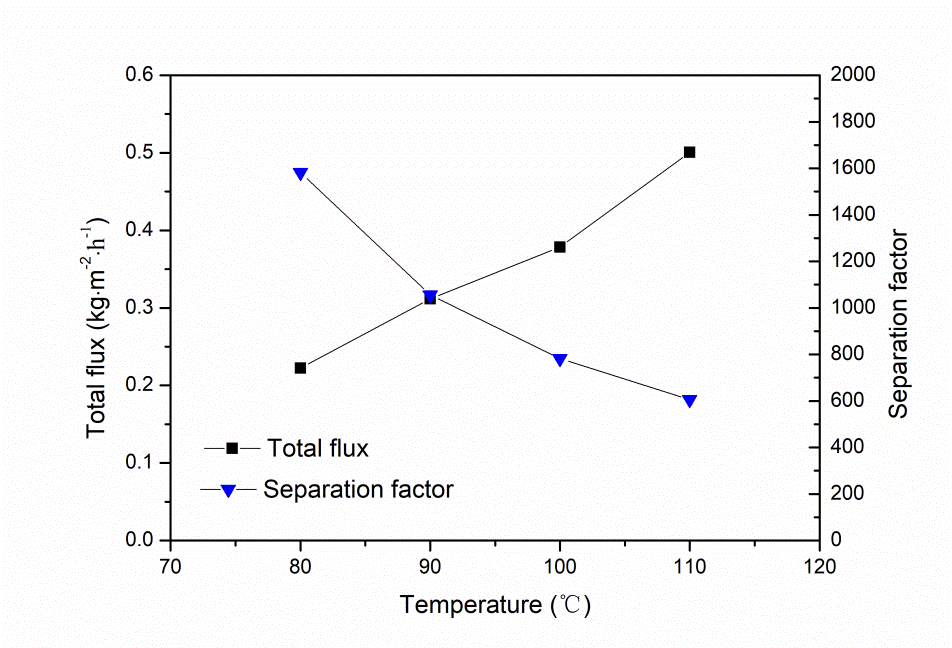
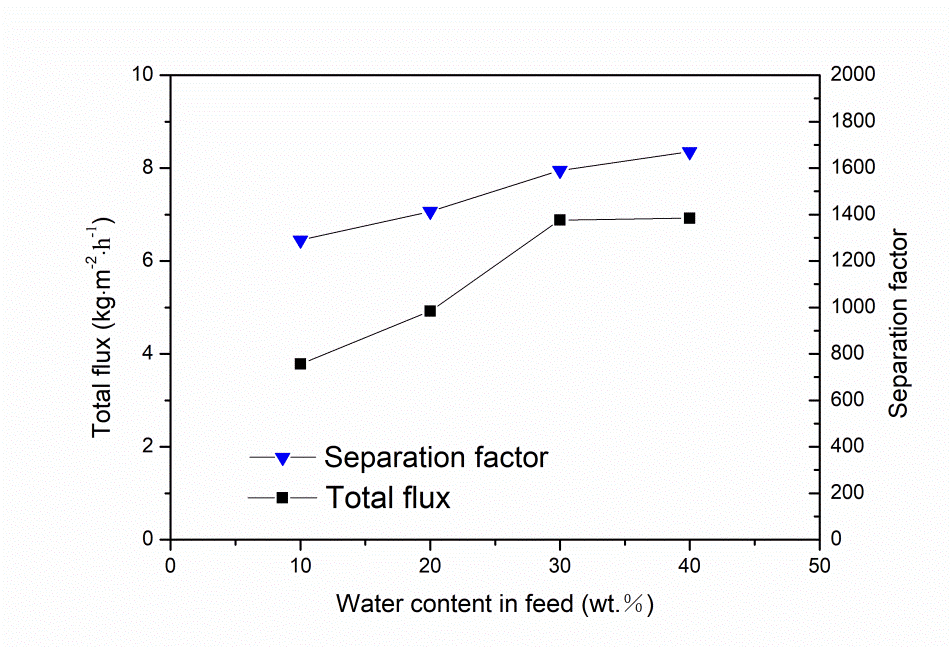
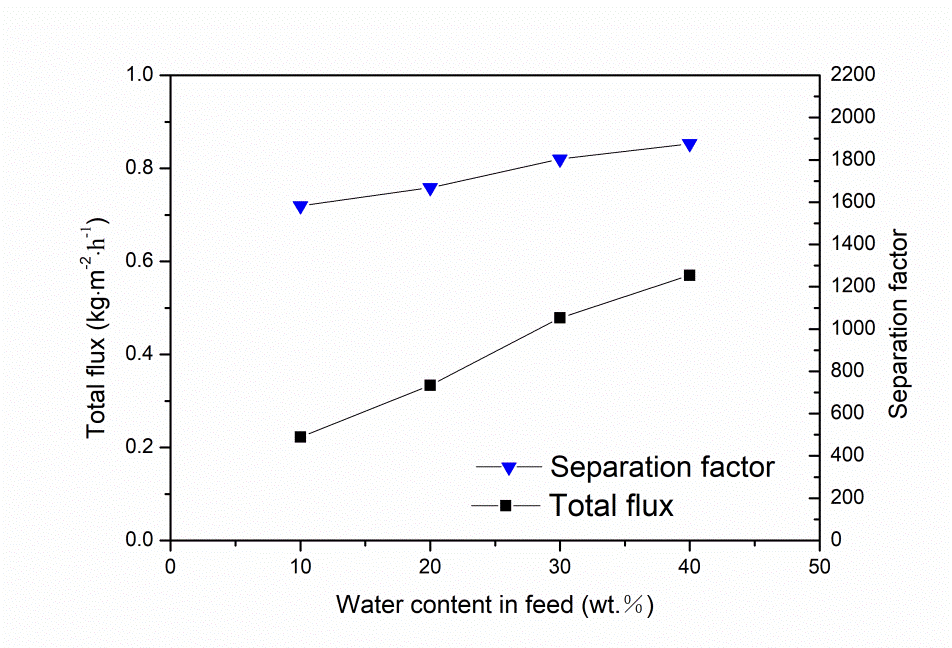
首先考察料液温度的影响,发现随着料液温度的升高,分子筛膜的渗透通量逐渐增加,分离因子下降。这是因为渗透组分在膜层表面的吸附效应减弱,在膜层内部扩散速率加快导致的。然后考察了料液水含量的影响,发现当水含量高于30 wt.%时,NaA分子筛膜的渗透通量不再增加,这是因为NaA分子筛膜表面吸附达到饱和。与NaA分子筛膜传质机理所不同的是,DDR分子筛膜在分离过程中依靠分子筛分,所以渗透通量随着料液水含量的增加而增加。最后研究两种分子筛膜在DMAc/水体系中渗透汽化稳定性,发现料液温度越高,分子筛膜的通量衰减越多。NaA分子筛膜通量衰减是因为DMAc在膜表面的竞争吸附与强电荷作用,堵住水通道。而DDR分子筛膜表现出良好的稳定性,这是因为一方面膜表面不吸附DMAc,另一方面DMAc不再受强电荷作用。
关键词:渗透汽化 分子筛膜 DMAc
ABSTRACT
With the increasing demand for organic solvents, solvent recovery and purification are particularly critical. Traditional organic solvent dehydration methods such as rectification and adsorption have problems such as complicated process flow, low separation efficiency, high energy consumption, and secondary pollution. Pervaporation is an energy-efficient membrane separation technology that is not limited by gas-liquid equilibrium and is suitable for the separation of azeotropic or near-boiling mixtures. The molecular sieve membrane has an average pore structure, good thermal stability and solvent resistance, and exhibits high flux and high selectivity in pervaporation dehydration separation.
In this paper, the effects of pervaporation operating conditions on the separation performance of hollow fiber NaA and DDR molecular sieve membranes and the pervaporation stability in dimethylacetamide/water system were investigated.
Firstly, the influence of the temperature of the feed liquid was investigated. It was found that as the temperature of the feed liquid increased, the permeation flux of the zeolite membrane gradually increased and the separation factor decreased.This is because the adsorption effect of the osmotic component on the surface of the film layer is weakened, and the diffusion rate inside the film layer is accelerated. Then, the influence of the water content of the feed liquid was investigated. It was found that when the water content was higher than 30 wt.%, the permeation flux of the NaA zeolite membrane no longer increased, because the surface adsorption of the NaA zeolite membrane reached saturation.The DDR molecular sieve membrane relies on molecular sieving during the separation process, so the permeation flux increases as the water content of the feed liquid increases. Finally, the pervaporation stability of two molecular sieve membranes in DMAc/water system was studied. It was found that the higher the temperature of the feed solution was, the more the flux of the zeolite membrane decayed. The flux attenuation of NaA zeolite membrane is due to the competitive adsorption and strong charge of DMAc on the membrane surface, blocking the water channel. The DDR zeolite membrane exhibits good stability because on the one hand the membrane surface does not adsorb DMAc, and on the other hand DMAc is no longer subjected to strong charges.
Key words:Pervaporation; zeolite membrane; DMAc
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1研究背景 1
1.2渗透汽化技术 1
1.2.1渗透汽化技术简介 1
1.2.2渗透汽化膜材料的分类与特点 1
1.2.3渗透汽化膜分离原理 2
1.2.4渗透汽化技术特点 2
1.2.5渗透汽化膜性能评价指标 3
1.2.6在有机溶剂脱水方面的现状 3
1.3中空纤维NaA分子筛膜 4
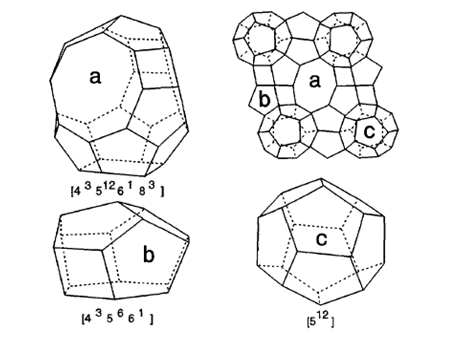
1.3.1沸石分子筛膜简介 4
1.3.2 NaA分子筛的特性 4
1.3.3 NaA分子筛膜的形成原理 5
1.3.4中空纤维NaA分子筛膜的合成 5
1.4中空纤维DDR分子筛膜 6
1.4.1 DDR分子筛的特性 6
1.4.2 DDR分子筛膜的研究进展 7
第二章 NaA、DDR分子筛膜用于二甲基乙酰胺渗透汽化脱水 9
2.1 引言 9
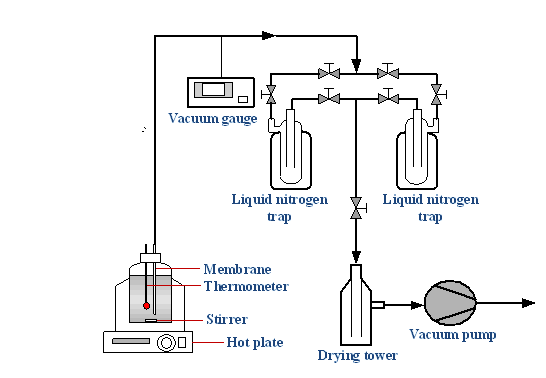
2.2 实验部分 9
2.2.1 实验原料及仪器 9
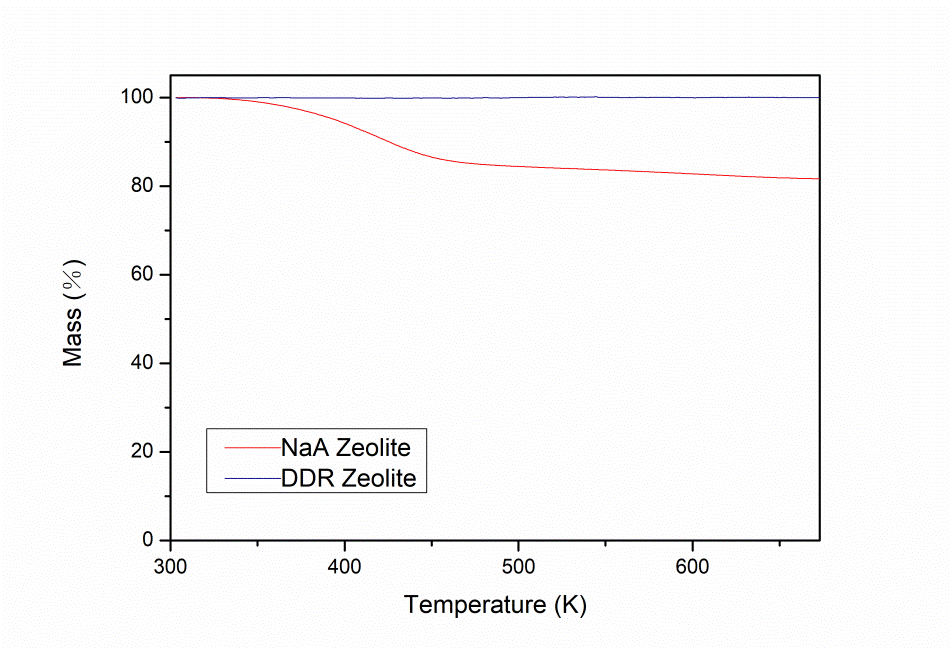
2.2.2分子筛膜的表征 10
2.3结果与讨论 12
2.3.1 操作温度的影响 12
2.3.2料液水含量的影响 13
2.3.3分子筛膜渗透汽化稳定性研究 15
第三章 结论 20
3.1结论 20
参考文献 22
致谢 25
第一章 文献综述
1.1研究背景
我国现在每年的有机溶剂使用量已超过亿吨,而在有机溶剂的运用中,水成为了主要杂质。传统运用的分离技术如精馏萃取等,都存在能耗高、工艺复杂、受气液平衡限制等缺点,而且分离效率较低,大多数有机溶剂都有毒有害,在分离过程中还可能会造成二次污染,对我国的生态环境造成了一定程度的破坏,所以现在急需一种节能环保、高效的分离技术。
膜分离技术不受气液平衡的限制,不用额外添加分离物质,所以被誉为21世纪具有战略价值的新技术。渗透汽化膜分离技术在工业有机溶剂脱水方面已经有了广泛的应用,并在很多工业有机溶剂体系中实现了工业化,体现了强大的应用潜力。
采用有机膜对溶剂进行脱水是一种成熟的技术,然而由于膜稳定性问题和溶胀效应,这些有机膜可能不适用于如二甲基乙酰胺等苛性溶剂。分子筛膜具有均一的孔道结构、良好的热稳定性和耐溶剂性,在渗透汽化脱水分离中表现出高通量及高选择性。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



