基于金属有机骨架材料MIL-101的串级催化剂的研制及其催化性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-22 19:46:53
摘 要
MIL-101除具有其它金属有机骨架材料所共有的孔隙率高、比表面积大、微孔尺寸可调以及结构易功能化的特点外,因其高水热稳定性,在非均相催化领域显示出了良好的应用前景。而近年来,串级催化在化工生产中的应用越来越广泛,串级催化剂的开发也被认为是解决反应系统一体化的关键,可以有效提高能源利用效率和减少三废排放。因此,合理利用MIL-101的易功能化和水热稳定性高的优势,拓宽串级催化剂的开发路径显得尤为重要。
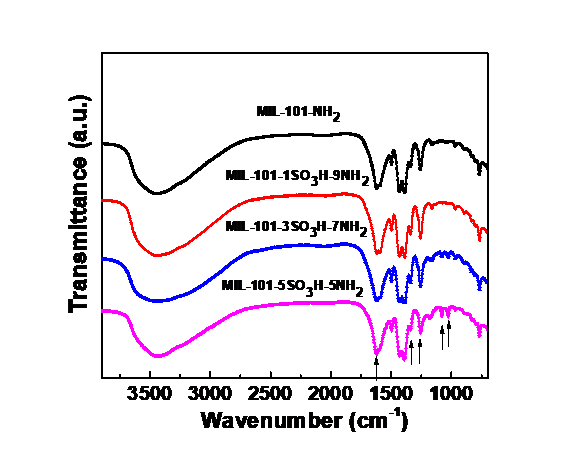
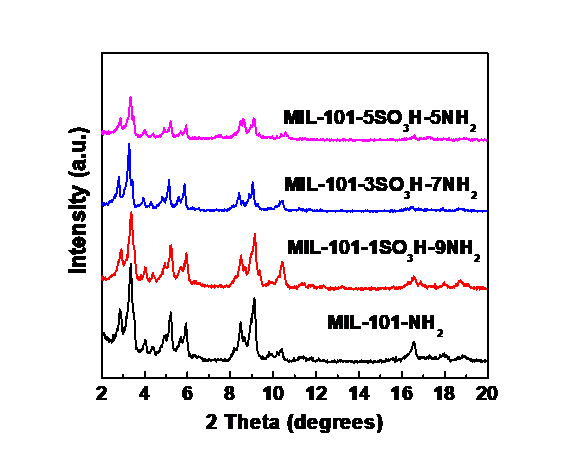
本研究详细介绍了通过原位合成法对进行功能化改性,借此引入不同配比的氨基和磺酸基功能位点,合成串级催化剂的过程。通过X射线衍射、傅里叶红外光谱、氮气吸附-脱附等温线等表征手段对样品的晶形结构、比表面积及孔体积进行了表征,以苯甲醛二甲缩醛生成苄烯丙二腈的串级反应为例探究了不同酸碱配比催化剂的催化性能。
研究结果表明,该方法可以有效合成不同酸碱配比的MIL-101-XSO3H-YNH2串级催化剂,保持原有的晶形结构,且在25℃,酸碱配比为1:9时取得了最佳的催化效果,相比,催化性能提升了 63.62%。
关键词:MIL-101 原位合成法 催化剂 串级反应
Preparation and Catalytic Performance of Cascade Catalysts Based on Metal-Organic Framework Material MIL-101
ABSTRACT
In addition to the high porosity, large specific surface area, adjustable pore size and easy functionalization of other metal-organic framework materials, MIL-101 is shown a good application prospect in the field of heterogeneous catalysis due to its high hydrothermal stability. In recent years, cascade catalysis has become more and more widely used in chemical production. The development of cascade catalysts is also considered to be the key to solving the integration of reaction systems, which can effectively improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions. Therefore, it is particularly important to make full use of the advantages of MIL-101's easy functionalization and high hydrothermal stability, and to broaden the development path of cascade catalysts.
This study details the process of synthesizing a cascade catalyst by functionally modifying MIL-101 by in-situ synthesis to introduce different ratios of amino and sulfonic acid functional sites. The crystal structure, specific surface area and pore volume of the sample were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherm and other characterization methods. The catalytic performance of different acid-base ratio catalysts was investigated by taking the cascade reaction of benzaldehyde dimethyl acetal to benzyl propylene malononitrile as an example.
The results show that the method can effectively synthesize MIL-101-XSO3H-YNH2 cascade catalysts with different acid-base ratios, and maintain the original crystal structure of MIL-101, The best catalytic effect was obtained at 25°C,and the acid-base ratio is 1:9. Compared with MIL-101-NH2, the catalytic performance was improved by 63.62%.
Keywords: MIL-101; In situ synthesis; Catalytic; Cascade reaction
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 1
1.1.1 1
1.1.2 2
1.1.3 2
1.2 3
1.2.1 4
1.2.2 6
1.3 7
第二章 9
2.1 9
2.2 9
2.2.1 9
2.2.2 11
2.3 12
2.3.1 12
2.3.2 12
2.3.3 12
2.4 13
第三章 14
3.1 14
3.1.1 14
3.1.2 15
3.1.3 16
3.2 18
3.3 21
第四章 22
4.1 22
4.2 22
参考文献 23
致 谢 27
1.1
金属有机骨架材料(Metal-Organic framework materials,MOFs)[1-3],是由与含N、O等的多齿有机配体组合而成的具有规律性网格结构的3D多孔配位聚合物[4]。与以往报道的多孔材料相比,具有更高的比表面积(1000-10000m2/g)和孔隙率(50%~90%),同时其微孔尺寸和拓扑结构可灵活调整,并且具有独特的配位结构,在多孔材料领域占据了非常大的比重,广泛应用于气体贮存[5]和分离[6],药物缓控投放[7],质子传输[8],传感器[9]和催化领域[10-13]。
1.1.1
20世纪60年代,有研究者[14]研究发现了具有三维网状结构的晶体,由硝酸根阴离子和金属配合物组成,这是MOFs材料第一次引发人们的关注,自此,MOFs的相关研究逐渐深入,到20世纪90年代初,Hoskins等[15, 16]以有机线形分子为配合物与金属离子进行配位,合成了理论上最初一代的MOFs材料,其比表面积较小,孔径分布较为简单,化学稳定性也不高,且骨架结构易坍塌,但即便如此,他们的首创性研究为MOFs材料的发展奠定了基础。
1995年,Yaghi课题组[17, 18]以三价钴为金属离子与均苯三甲酸合成了一种具有可逆吸附性能的MOFs材料,并且首次提出“MOFs”的概念,该材料能够针对性地吸附客体分子,并且在脱附后骨架基本结构不会改变,具有良好的结构稳定性。1997年,Kitagawa课题组[19]合成了首个具有立体构造的MOF,在气体吸附方面得到许多应用。直到20世纪末,MOF-5[20]和HKUST-1[21]的合成将MOFs研究引入了一个新的阶段。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



