剧烈塑性变形制备超细晶纯铜的耐海水腐蚀性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-23 20:05:20
摘 要
铜及铜合金由于具有良好的导电、导热、耐腐蚀性能等,被广泛的应用于航空航天,海洋工程,石油化工等领域。剧烈塑形变形(SPD)技术能够在大幅度降低晶粒尺寸的同时,提高材料的力学性能、耐腐蚀性能等,而被广大学者所关注。本工作主要通过等通道角挤压(ECAP)制备超细晶铜,采用慢应变速率拉伸实验,测试材料的应力腐蚀敏感性以及强度特征,运用电子背散射衍射技术来定量分析晶粒尺寸以及晶界特征分布对材料应力腐蚀敏感性的影响,扫描电子显微镜用来分析试样的断口形貌特征。通过上述实验,得出以下结论:
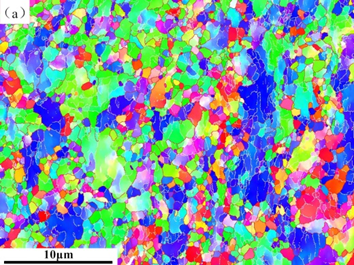
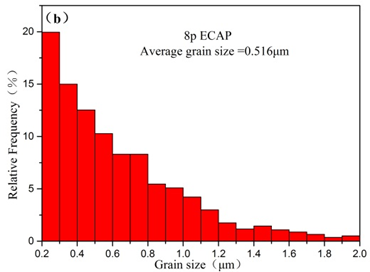
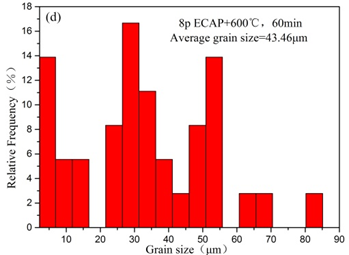
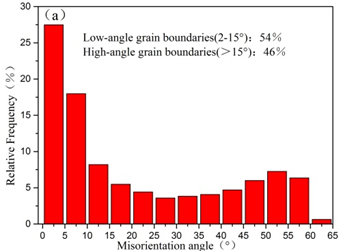
1)纯铜经过ECAP加工后,晶粒尺寸大幅度降低,由粗晶状态降低到516nm,晶界密度大幅度提高,小角度晶界分数达到54%;经过退火后晶粒长大,平均晶粒尺寸达到43.46μm,晶界则以大角度晶界为主。
2)纯铜经过ECAP、ECAP 轧制、退后处理后,屈服强度和拉伸强度先增加后降低,ECAP 轧制后的屈服强度和抗拉强度最大,而材料的塑形则呈现相反的趋势。
3)通过慢应变速率拉伸测试可知,不同加工状态的应力腐蚀敏感性分别为:原始纯铜的0.8820,ECAP的0.5648,ECAP 轧制的0.7920以及ECAP 退火的0.9785。其中ECAP 退火试样的抗应力腐蚀敏感性最好。
关键词:纯铜 ECAP 应力腐蚀敏感性 晶粒尺寸
Abstract
Copper and copper alloys are widely used due to their good corrosion resistance. The severely shaped deformation (SPD) technology can greatly improve the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of materials while greatly reducing the grain size, which has attracted the attention of scholars. In this work, ultra-fine crystal copper was prepared by equal channel angular extrusion (ECAP). The stress corrosion sensitivity of the material was measured by slow strain tensile test. The grain size was analyzed by electron backscatter diffraction technique. The fracture morphology of the sample was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy. Through the above experiments, the following conclusions are drawn:
1) After ECAP processing, the grain size of the pure copper is greatly reduced, from the coarse crystal state to 516 nm, the grain boundary density is greatly improved, and the small-angle grain boundary fraction reaches 54%. After annealing, the grain grows up to 43.46 μm, mainly high-angle grain boundaries.
2) After ECAP, ECAP rolling and post-treatment, the strength first increases and then decreases. The yield strength and tensile strength of ECAP after rolling are the largest, while the shape of the material shows the opposite trend.
3) The slow-strain tensile test shows that the stress corrosion sensitivities of different processing states are: 0.8820 of original pure copper, 0.5648 of ECAP, 0.7920 of ECAP rolling, and 0.9785 of ECAP annealing. Among them, ECAP annealed samples have the best resistance to stress corrosion.
Key words: pure copper; ECAP; Stress corrosion susceptibility; grain size
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景 1
1.2 超细晶材料的制备方法 1
1.2.1 ECAP 1
1.2.2累积叠轧焊 (ARB) 2
1.2.3高压扭转 (HPT) 3
1.2.4 表面机械研磨处理(SMA) 4
1.3超细晶铜的性能特点 5
1.4. 腐蚀性能研究概况 5
1.4.1 金属腐蚀的分类 5
1.4.2 铜及铜合金应力腐蚀研究进展 6
1.5 研究目的与研究意义 7
第二章 实验材料和实验方法 8
2.1 实验材料 8
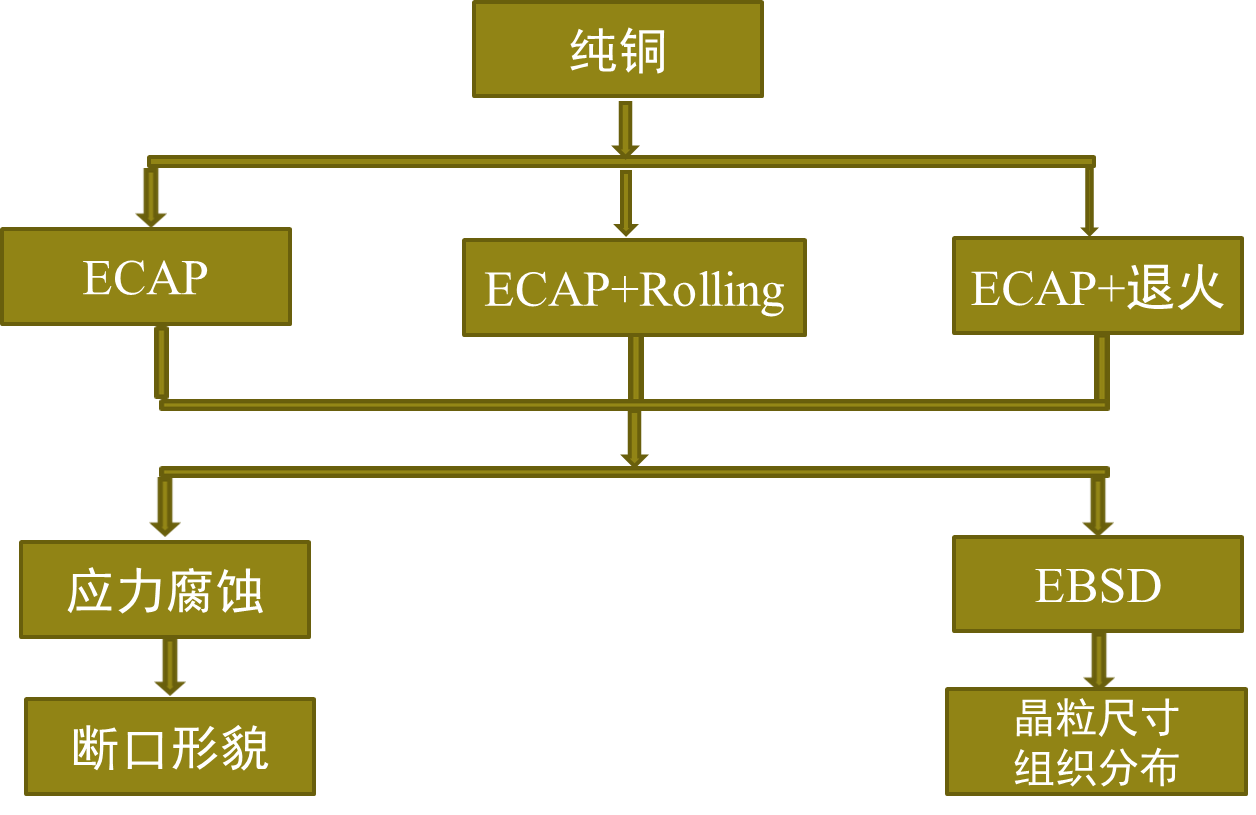
2.2 技术路线 8
2.3实验方法 8
2.3.1 ECAP 8
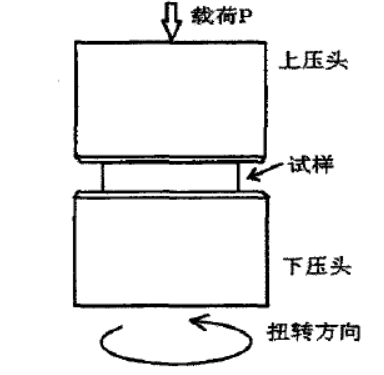
2.3.2 背散射衍射实验EBSD 8
2.3.3 应力腐蚀 9
2.3.4 扫描电子显微镜 9
第三章 实验结果和讨论 10
3.1 显微组织观察 10
3.1.1 ECAP的显微组织 10
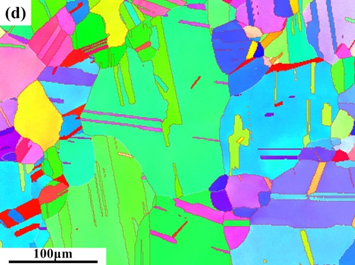
3.1.2 ECAP 退火背散射衍射微观组织观察 10
3.1.3大小角晶界占比 11
3.2 应力腐蚀 11
3.2.1原样的应力腐蚀情况 12
3.2.2 ECAP的应力腐蚀情况 12
3.2.3ECAP Rolling的应力腐蚀情况 13
3.2.4退火后的腐蚀情况 14
3.3 断口形貌的观察 16
3.3.1纯铜的断口形貌 16
3.3.2 ECAP的断口形貌 16
3.3.3 ECAP Rolling的断口形貌 17
3.3.4 ECAP 退火后的断口形貌 18
第四章 结论 20
第五章 展望 21
参考文献 22
致 谢 24
第一章 绪论
1.1研究背景
铜是人类最早使用的金属之一。早在距今六千多年以前,我们的祖先就学会采掘铜矿,并通过冶炼浇铸制造器皿、兵器和生产工具。中国在商周时就己经掌握了精湛的冶金和加工工艺,留下了许多精美的工艺品。铜和铜合金因具有优秀的导电性、导热性、观赏性、耐蚀性等优点而被大规模应用于现代工程技术领域,普遍应用于机械制造、电子、建筑、化工、能源、国防工业等领域[1]。它们己经是生产及生活中不可替代的重要工程材料。除此之外,铜及其合金的种类及消费产量也己成为了衡量一个国家工业技术水平的重要指标之一。
近年来,人们相继开展对纯铜及铜合金的研宄,但是实际应用的却很有限。因为纯铜的强度并不高,在使用的过程中难以充当大的零件,多是以细小零部件为主,其抗拉强度大约在350MPa,经过软化处理后,纯铜的抗拉强度会大大降低,而且纯铜的导热性和耐腐蚀性并不算突出。虽然采用添加一些合金元素的方法可以使铜合金的力学性能得到改善,但这会降低铜合金的导电性。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



