层状多晶TiS2材料的高速剪切与有机杂化处理及其热电性能毕业论文
2020-04-23 20:16:06
摘 要
二硫化钛 (TiS2) 是一种具有层状结构的热电材料,具有良好的电输运性能,功率因子能与碲化铋等目前最好的热电材料相媲美,但其本身的晶格热导率较高,导致热电优值相对偏低,尚未达到实际应用水平。为降低其晶格热导率,本课题采用室温下溶液中高速剪切的技术手段,可在获得粒度细化的同时,避免传统高能球磨易产生非晶化和片晶形貌破坏而导致电输运性能降低的现象。
本论文旨在低温高速剪切方法基础上,通过往剪切液中加入一定比例己胺等有机物,考察这些添加剂辅助下TiS2剪切产物的颗粒尺寸、形貌、结晶度以及烧结体的电输运性能,初步探明有机物的合理添加比例及作用机理。通过对比相同剪切工况条件下(固液比例、剪切速度与时间等)、有机物不同添加量的研究结果发现:
- 加入10 mol% (相对TiS2) 己胺剪切所得粉体,保持高度结晶度,平均粒度从34 μm降低至3 μm左右;但由于有机物残留对电子传输的影响,其放电等离子烧结块体的电导率低下;
- 在Ti2 : HA = 1 : (0.01~0.05)范围内,烧结样品电导率随有机物含量增加持续下降,塞贝克系数持续增大,而功率因子明显降低。加入1 mol%己胺剪切所得粉体,结晶度高且平均粒度与纯乙醇剪切物相比变化不大,烧结所得块体保持了良好的电输运性能:(1) 与纯乙醇剪切产物的烧结样品相比,电导率下降约40%,而塞贝克系数明显提高,说明有机物部分残留且增强了电子散射;(2) 与未剪切粉体烧结样品相比,电导率略低而塞贝克系数增加显著,原因可归结于织构度提升和有机物残留对电输运相反作用的综合结果;得益于电子热导率的有效降低和较高的功率因子,ZT 673K达到0.55,比未剪切粉体烧结样品提高约40%,并与纯乙醇剪切粉体烧结样品性能持平。
以上研究表明,高速剪切可以提升TiS2块体的电输运性能,HA的适量添加 (约1 mol%)可有效调节电输运性能、降低电子热导率的同时维持较高的功率因子。
关键词: 热电材料; 二硫化钛; 有机物辅助剪切; 电输运
ABSTRACT
As a layer-structured material, titanium disulfide (TiS2) has excellent electrical transport properties and its power factor is comparable to that of the best traditional thermoelectric (TE) materials. However, due to its own high lattice thermal conductivity, its TE figure of merit (ZT) is still insufficient to meat the requirement for practical application. To reduce the lattice thermal conductivity, an approach of room temperature mechanical exfoliation in a solution has been adopted, which would down-size the grains while avoiding the performance degradation due to amorphization and morphology destroy that usually occur in an ordinary top-down high-energy ball-milling process.
This work aimed to explore the effect of organic additives like HA on the exfoliated powder’s crystallinity, morphology, and most importantly the electrical transport performance of its sintered bulk ceramics, and thus to clarify the appropriate amount of the additive and its mechanism. From comparative investigation into the experimental results with a same operation parameter of the exfoliation (solid to solution mass ratio, rotating speed and time and etc.) but with different organic addition, results show:
- Powders after exfoliation in an ethanol solution with 10 mol% HA (to the mass of TiS2) showed a high crystallinity without obvious amorphization, the average grain size decreased from 34 μm to about 3 μm; the SPS-sintered bulk sample’s electrical conductivity was low due to the presence of organic residue.
- With the increase of HA addition in the range of TiS2 : HA = 1 : (0.01~0.05), the electrical conductivity decreased while Seebeck coefficient increased remarkably, and the power factor got suppressed continuously. Using the powders after exfoliation in an ethanol solution with 1 mol% HA that exhibited a similarly high crystallinity and grain sizes to the powder exfoliated in pure ethanol, the sintered ceramic sample showed relatively high electrical performances: (1) as compare with that of samples sintered using powder treated in pure ethanol, the electrical conductivity is 40% lower while the S is notably higher, suggesting a strengthened carrier scattering due to the organic impurities; (2) compared with that of pristine TiS2 sintered samples, electrical conductivity slightly decreased while the S was 40% larger, probably caused by the combined effects of the increased texture and the organic impurities. As a result, the ZT value of this sample reached 0.55 at 673 K, which is almost 40% higher than that of the pristine counterpart and comparable to that of the sample sintered using power exfoliated in pure ethanol.
These results tend to conclude that the aid of organic additive (HA) can affect notably the transport properties with a suppression of electrical thermal conductivity and a maintained high power factor.
KEY WORDS: Thermoelectric; Titanium disulfide; Organic-aided exfoliation; Electrical transport
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 课题研究背景 1
1.2 热电理论 1
1.2.1 塞贝克效应 1
1.2.2 珀尔帖效应 1
1.2.3 热电材料性能参数 2
1.3 TiS2体系热电材料 2
1.4 热电性能优化方法 4
1.5 本课题研究内容 5
第二章 实验部分 6
2.1 有机物的选择 6
2.2 实验原料与设备 6
2.2.1 实验原料 6
2.2.2 实验仪器设备 7
2.3 实验流程 8
第三章 结果与讨论 11
3.1 TiS2 : HA : DMSO = 1 : 2 : 3剪切结果与分析 11
3.2 TiS2 : HA : DMSO = 1 : 0.2 : 0.5等剪切结果 12
3.2.1 剪切结果与分析 12
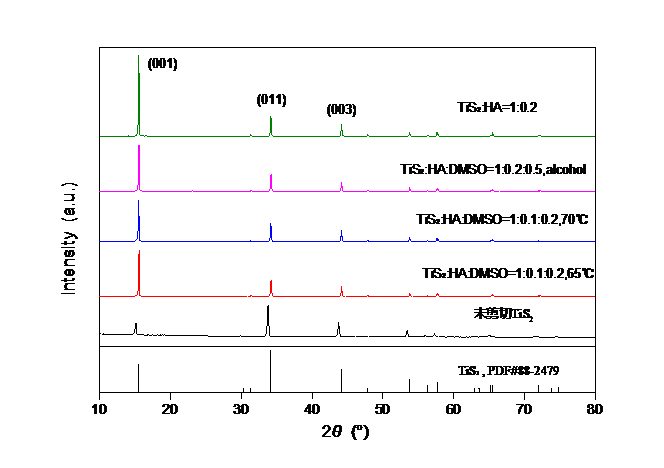
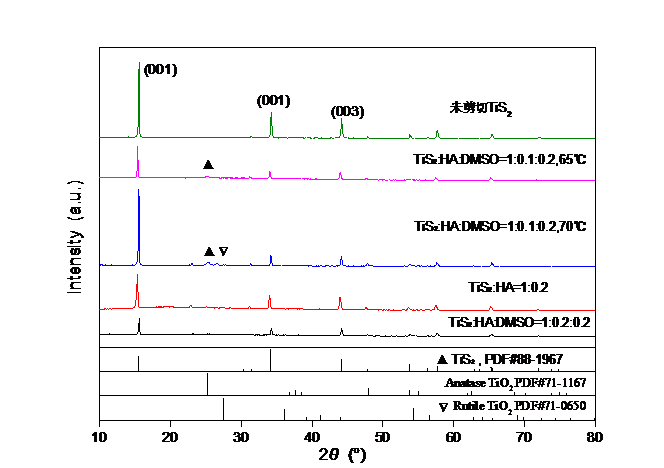
3.2.2 XRD分析 13
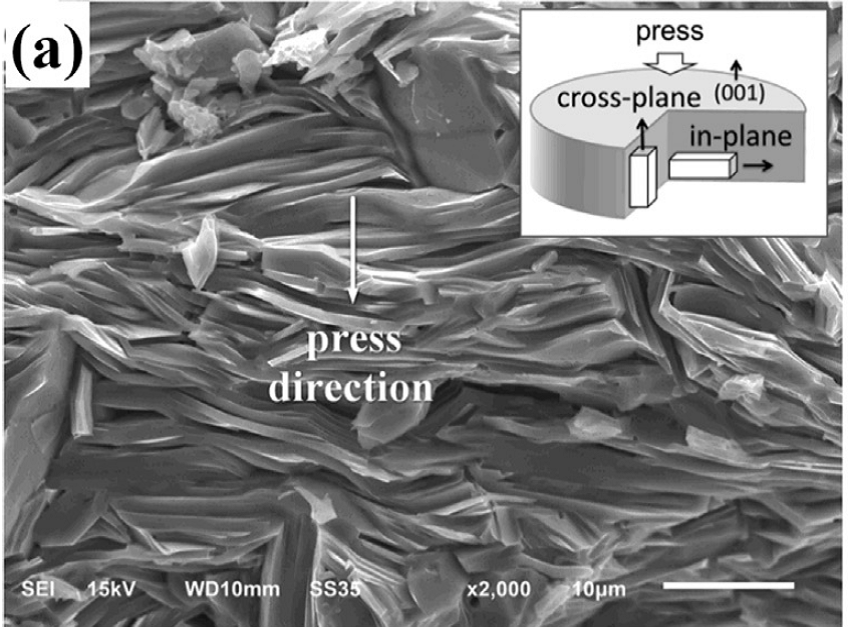
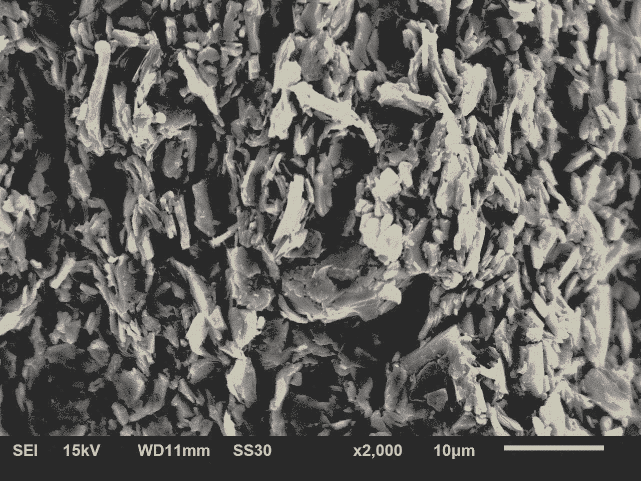
3.2.3 扫描电镜分析 15
3.2.4 电输运性能分析 16
3.3 TiS2 : HA = 1 : 0.01等剪切结果 17
3.3.1 剪切结果与分析 17
3.3.2 XRD与粒度分析 18
3.3.3 致密度分析 20
3.3.4 电输运性能分析 20
3.3.5 导热性能分析以及ZT值 22
第四章 结论 24
参考文献 25
致 谢 28
第一章 绪论
1.1 课题研究背景
由于传统的石化燃料造成的污染非常严重,并且其供应也日益吃紧,人们迫切希望能够找到一种新型材料以缓解能源危机。热电材料作为一种功能材料,既可利用热能进行温差发电,又可通以电流实现静态制冷与加热,故而能走入人们的视线。许多国家都非常重视热电材料方面的研究,将其列为重大发展项目,未来热电材料将会是新型材料发展的一个重点[1,2]。而目前已经成功投入应用的热电材料主要是Bi2Te3基的材料[3],虽然它具有较好的热电性能,但是由于碲化铋本身合成成本昂贵,且它是中等毒性物质,这是Bi2Te3基热电材料的不足之处[4]。因此,我们希望能够开发出一种环境友好型热电材料。它既具有良好的热电性能,同时又具有较低的毒性或者最好没有毒性,并且生产成本也相对低廉。
1.2 热电理论
1.2.1 塞贝克效应
1821年德国科学家发现,当两种不同导体构成的闭合回路时,加热导体的一端,会形成一个ΔV的电动势,此时导体间的温度差为ΔT,这一现象就是塞贝克效应[5]。当温度差ΔT较小时, ΔV与ΔT成正比, 比例系数就是塞贝克系数 (单位: V/K),其公式为:
S= ΔV/ΔT (ΔT → 0) (1-1)
相关图片展示:

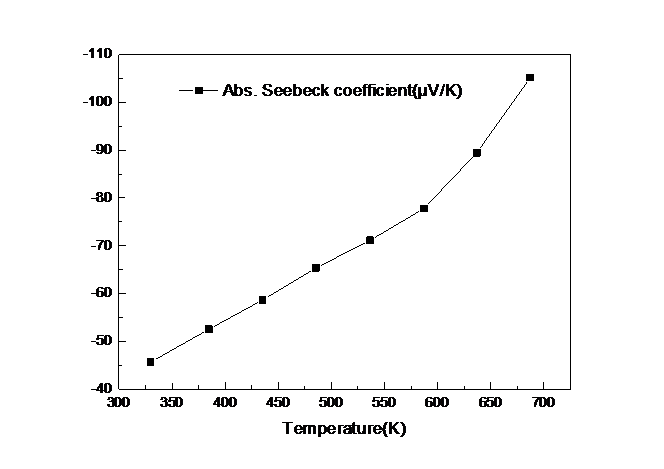
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



