解磷菌株的筛选及促生效应的研究毕业论文
2020-04-26 12:48:40
摘 要
对植物来说,磷是生长过程中不可缺少的营养元素。解磷菌能够分解土壤中有机磷化合物为有效磷,从而有利于植物的生长。
为了提高土壤中磷的含量,使植物更好的生长,本实验取已初筛的2株解磷菌B9(节杆菌)、TF4(死亡谷芽孢杆菌)进行摇瓶复筛,以此来探究摇瓶内解磷菌能否将无机磷转变为有机磷,通过解磷菌盆栽试验,观察解磷菌对植物有无促生作用并探究解磷菌能否将土壤中无机磷转化为有机磷,从而找出解决植物磷素供应问题的一条有效途径。
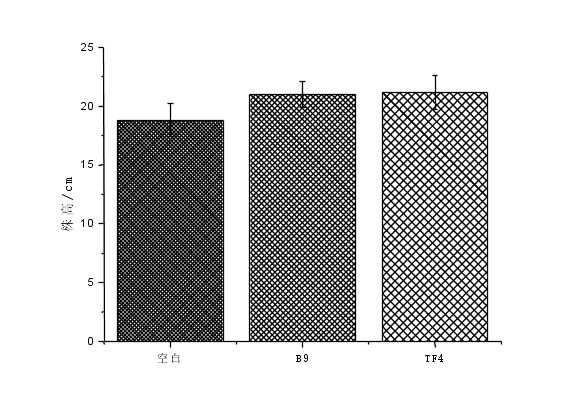
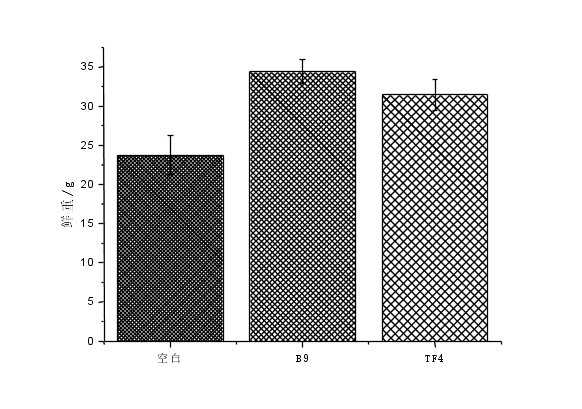
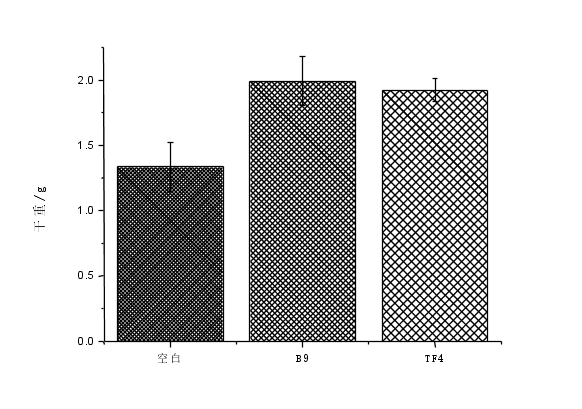
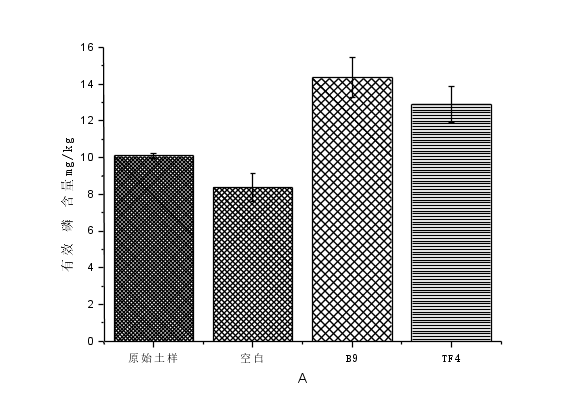
结果表明,接种B9、TF4菌株的两个处理组均能改善黑叶葵扇白菜生物性状,增加黑叶葵扇白菜的株高,鲜重和干重,增加土壤有效磷含量。接种B9菌株的土样黑叶葵扇白菜株高、鲜重、干重分别增加了11.81%、44.62%、49.12%;接种TF4菌株的土壤与对照组相比,黑叶葵扇白菜的株高、鲜重、干重分别增加了9.72%、32.24%、43.88%。接种了B9菌株的土壤与对照组相比有效磷含量增加了70.98%。接种TF4菌株的土壤与对照相比土壤有效磷含量增加53.74%。总体看,B9、TF4都能改善土壤微环境,提高作物产量。
关键词:解磷菌 盆栽试验 微生物肥料
Screening and growth promoting effects of phosphate-dissolving strains
ABSTRACT
For plants, phosphorus is an indispensable nutrient for growth. In order to promote the growth of plants, Phosphate solubilizing bacteria decompose organic phosphorus compounds into organic phosphorus
In order to improve the phosphorus content in the soil and make the plants grow better, this experiment takes two strains of phosphate-dissolving bacteria B9 and TF4 for shake flask re-screening, in order to explore whether the phosphate-dissolving bacteria in the shake flask can The inorganic phosphorus is converted into organic phosphorus, and the pot-phosphorus bacteria pot experiment is carried out to observe whether the phosphate-dissolving bacteria have a promoting effect on plant roots and find an effective way to solve the problem of plant phosphorus supply.
The results showed that the two treatments of B9 and TF4 could improve the biological characteristics of Chinese cabbage, increase the plant height, fresh weight and dry weight of Chinese cabbage, and increase the available phosphorus content in soil. The soil inoculated with B9 strain increased by 11.81%, 44.62% and 49.12%.The soil to which TF4 bacteria was applied was 9.72%, 32.24%, and 43.88%. Furthermore, the soil available phosphorus content increased by 70.98% compared with the control. The inoculated TF4 strain increased the soil available phosphorus content by 53.74% compared with the control. In a word, B9 and TF4 can ameliorates the soil microenvironment and enhance crop yield .
Key words: Phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria ;Pot experiment;Microbial fertilizer
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景 1
1.2微生物肥料 1
1.2.1微生物肥料分类 2
1.2.2微生物肥料作用机理 2
1.2.3 微生物肥料优点及作用 2
1.3解磷菌 2
1.3.1解磷菌分类 3
1.3.2解磷菌作用机理 3
1.4本论文的研究目的及内容 4
1.4.1本课题的目的及意义 4
1.4.2本课题的主要研究内容 5
第二章 实验材料与方法 6
2.1实验材料 6
2.1.1实验主要试剂 6
2.1.2实验主要仪器 7
2.2培养基 8
2.3实验方法 8
2.3.1解磷菌的复筛 8
2.3.2盆栽实验 8
第三章 结果与讨论 10
3.1菌株特征 10
3.1.1菌株形态 10
3.1.2菌株的生理生化特征 12
3.1.3菌株的16S rDNA鉴定 13
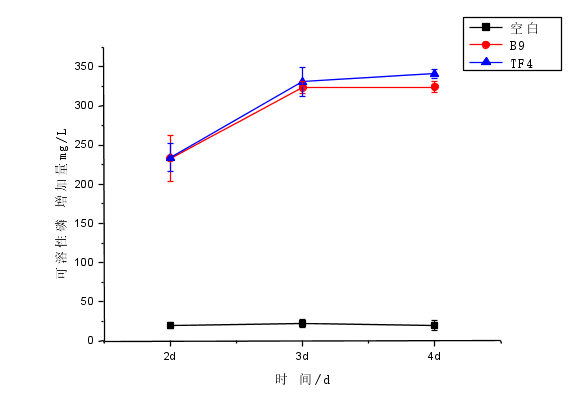
3.2溶液中解磷效果验证 14
3.3促植物生长的效果评估 15
3.3.1黑叶葵扇白菜的株高 15
3.3.2黑叶葵扇白菜的鲜重 16
3.3.3黑叶葵扇白菜的干重 17
3.3.4土壤有效磷含量 18
3.3.5土壤pH 18
第四章 结论与展望 19
4.1结论 19
4.2展望 19
参考文献 21
附录 相关标准曲线 24
致 谢 26
第一章 绪论
1.1研究背景
磷是植物细胞的重要组成元素,在植物的生长过程中扮演者重要角色。我国的气候条件极易生成富含Fe、Al元素的土壤,Fe3 、Al3 固定住难溶性磷,难溶性磷酸盐形成,而雨水带走了可溶性磷,致使山地严重缺乏磷元素,再加上磷肥被农民不科学的施用,导致土壤板结更加严重、土壤更加缺磷。
然而,解磷微生物具备将土壤中难溶性磷酸盐分泌为植物生长所需的生长素类物质的能力[1],即对植物生长发育有促进作用。因为这一特点,解磷微生物菌剂的生产或成为解决我国缺磷问题的一条有效途径。
相关图片展示:

课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



