陶瓷纳滤膜用于壳寡糖分离纯化的研究毕业论文
2020-04-26 12:49:40
摘 要
功能性低聚糖对人体健康有重要作用。其中壳寡糖具有好的水溶性和生物活性,平均分子量小于3000 Da,能够改善肝脏和心肺功能及其他多种生理功能,增强对人体的免疫调节,还可以用于抗肿瘤、预防三高。因此近年来壳寡糖被广泛用于食品和医药领域。目前市面上的壳寡糖是由壳聚糖酶解得到,含有未分解的壳聚糖,酶以及氨基葡萄糖等杂质。因此需要引入新的分离、提纯方法提高壳寡糖纯度。膜分离法在低聚糖的分离纯化工程中已经取得了一定进展,而且膜分离过程与传统的纯化分离手段相对比具有能量消耗少、分离效率高、操作简便、自动化程度高等诸多优势。而随着各种应用体系对于膜分离过程的分离精度和膜材料稳定性要求日益严苛,陶瓷膜孔径分布窄而分离精度高,材料稳定而机械强度高、化学稳定性好、热稳定性好的优势也逐渐显现出来。陶瓷膜的分离机理是以尺寸筛分为主,据此,本文研究了以尺寸筛分为主导的以壳寡糖为代表的低聚糖类的分离与纯化。而膜污染是膜分离过程的主要障碍。膜污染是指在使用过程中,尽管操作条件保持不变,但由于膜表面形成了吸附层或膜孔堵塞等外部因素导致膜性能下降的现象。膜污染分为机械堵塞、吸附和沉积作用以及浓差极化,不同膜的膜污染原因也不同。本文采用陶瓷膜对壳聚糖酶解液进行纯化。通过对壳聚糖酶解液体系的表征,选择采用5 nm的单管陶瓷膜进行分离纯化。采用实验室自制分离装置进行陶瓷膜截留性能和纯水渗透通量的表征,对料液浓度、跨膜压差、膜面流速、操作温度等操作条件的影响进行了研究,在综合考虑了分离效率、分离精度、能耗、膜管使用寿命等因素后确定了最优条件并对过滤过程的稳定性进行了考察。经过操作条件的优化,确定了料液浓度为15 g/100 g,操作压力为0.6 MPa,膜面流速为0.8 m·s-1,操作温度为45 °C。5 nm对蛋白的截留效果良好,但对壳寡糖有一定截留。在一系列实验过程中,陶瓷膜在经受次氯酸钠和纯水的清洗后膜渗透性能和分离效果均保持稳定。本文工作希望为陶瓷膜在制备高纯度壳寡糖中的推广和规模化应用提供数据支撑。
关键词:陶瓷膜 纳滤膜 壳寡糖 纯化 膜污染 低聚糖
Application of ceramic nanofiltration membrane in separation and purification of Chitosan-oligosaccharide
Abstract
Functional oligosaccharide plays an important role in human health. Chitosan oligosaccharide has good water-solubility and biological activity, and its average molecular weight is less than 3000 Da, which can improve liver, cardiopulmonary function and other physiological functions, enhance the immune regulation of human body, and can also be used for anti-tumor, prevention of hypertension, hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia. So chitosan oligosaccharide is widely used in food and medicine fields in recent years. Currently, chitosan oligosaccharides in the market are obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis of chitosan, containing impurities such as undecomposed chitosan, enzyme and glucosamine. So it is necessary to introduce new methods of separation and purification to improve the purity of chitosan oligosaccharide. Membrane separation has made some progress in the separation and purification of oligosaccharides, and the membrane separation process has many advantages, such as less energy consumption, high separation efficiency, simple operation and high degree of automation. However, with the increasingly stringent requirements of various application systems on the separation accuracy and stability of membrane materials, the advantages of stable materials with high mechanical strength, chemical stability and thermal stability have gradually emerged. The separation mechanism of ceramic membrane is mainly based on size screening, so this paper studied the separation and purification of oligosaccharides represented by chitosan oligosaccharides. Membrane contamination is the main obstacle to membrane separation. Membrane fouling refers to the phenomenon that the membrane performance decreases due to external factors such as adsorption layer or membrane hole blockage, although the operating conditions remain unchanged during the use. Membrane fouling can be divided into mechanical plugging, adsorption and deposition, and concentration polarization. In this paper, chitosan enzymatic hydrolysate was purified by ceramic membrane. By characterizing the liquid system of chitosan enzymatic hydrolysis, 5 nm single tube ceramic membrane was selected for separation and purification. Using ceramic membrane separation device made by the laboratory intercept performance and characterization of pure water permeation flux, the concentration of slurry, transmembrane pressure difference, velocity at the membrane surface, operating temperatures are studied, the influence of operating conditions, such as considering the separation efficiency, separation precision, power consumption, the service life of the membrane tube after factors such as the optimum conditions were determined and the stability of the filtering process was investigated. After optimization of operating conditions, the concentration of feed liquid was determined to be 15 g/100 g, the operating pressure was 0.6 Mpa, the film surface velocity was 0.8 m·s-1, and the operating temperature was 45 °C. 5 nm had a good rejection effect on protein, but it had some rejection on chitosan oligosaccharide. In the course of a series of experiments, the permeability and separation effect of ceramic membrane remain stable after being cleaned by sodium hypochlorite and pure water. The work in this paper hopes to provide data support for the promotion and large-scale application of ceramic membrane in the preparation of high-purity chitosan oligosaccharides.
Key words: ceramic membrane;nanofiltration membrane;chitosan;purification;membrane fouling;oligosaccharides
目 录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1膜分离法用于低聚糖类分离的研究进展 1
1.2膜污染 2
1.2.1机械阻塞 3
1.2.2吸附和沉积作用 3
1.2.3浓差极化 3
1.2.4膜的清洗与再生 4
1.3壳寡糖的制备、性质、应用、分离 4
1.3.1壳寡糖的性质 4
1.3.2壳寡糖的应用 5
1.3.3壳寡糖的制备 5
1.3.4壳寡糖的分离方法 6
1.3.5 小结 7
1.4研究方法和目的 8
第二章 实验 9
2.1 引言 9
2.2 实验部分 9
2.2.1实验用陶瓷膜与试剂 9
2.2.2实验仪器与装置 10
2.2.3实验方法 10
2.3结果与讨论 11
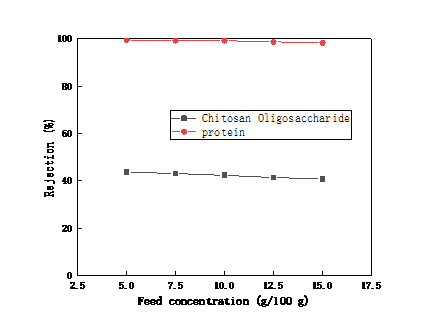
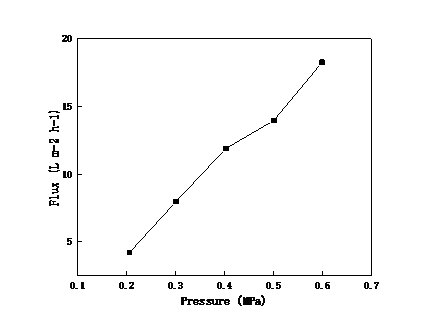
2.3.1料液浓度对陶瓷膜截留效果和渗透性能的影响 12
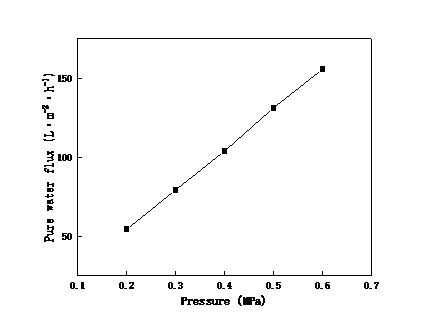
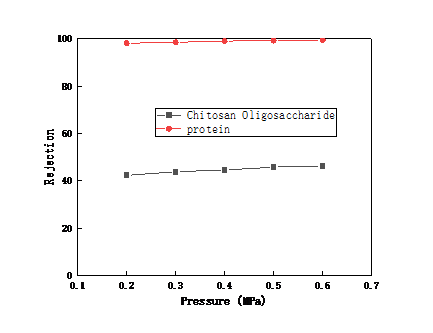
2.3.2 跨膜压差对陶瓷膜截留效果和渗透性能的影响 13
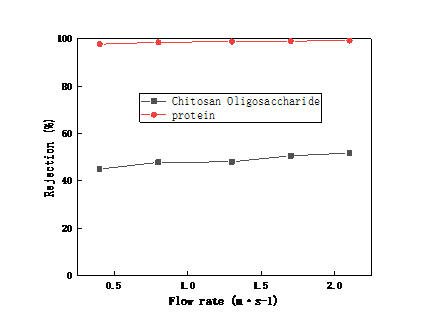
2.3.3膜面流速对陶瓷膜截留效果和渗透性能的影响 14
2.3.4温度对陶瓷膜截留效果和渗透性能的影响 15
2.3.5膜分离过程稳定性考察 15
2.3.6膜管清洗 16
2.4本章小结 16
第三章 结论与展望 18
参考文献 19
致谢 22
- 绪论
1.1 膜分离法用于低聚糖类分离的研究进展
聚合度低(2~10)的糖称为低聚糖。低聚糖分为50型低聚糖和90型低聚糖(低聚糖含量分别在50%和90%左右),其中,不被人体酶解,在小肠中不被吸收的称为功能性低聚糖,常见的功能性低聚糖有低聚果糖(果寡糖)、壳寡糖、低聚木糖(木寡糖)、大豆低聚糖、低聚异麦芽糖、低聚半乳糖、棉籽糖和水苏糖等[1]。传统方法制备(酶法和低聚糖植物提取)的低聚糖基本上是含有较多杂质的50型低聚糖。因此,功能性低聚糖行业所面临的重大难题是如何将50型低聚糖纯化为90型低聚糖。相比于传统的分离方法,膜分离法具有分离效率高、操作简单、能耗较低、无二次污染等优势,因而在低聚糖类的分离纯化过程中具有广阔的应用前景[2]。
膜分离法分离壳寡糖尚未得到普及,未能推广到工业化应用,而将膜分离用于高纯度低聚糖的制备工艺,已有不少相关人员对此行了研究。江楷煜等采用超滤-纳滤偶联膜分离技术高效制备低聚糖阿魏酸酯和香豆酸,阿魏酸酯透过率超90%,香豆酸透过率超80%[3]。Machado等[4]联用纳滤和微滤来提纯朝鲜蓟提取物中的低聚果糖,糖类物质几乎100%透过的同时大分子杂质被截留。Ledur Alles等[5]联用超滤和纳滤工艺浓缩提纯从雪莲果根茎中提取的低聚果糖,澄清效果较好,但约15%的低聚果糖被截留不利于产品收率的提高。
相关图片展示:
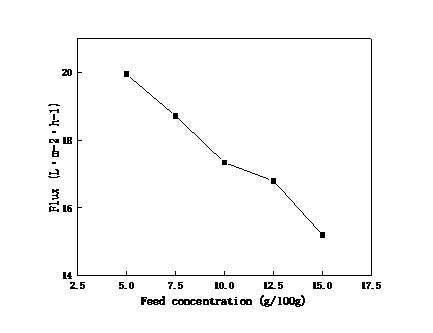

课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



