四通道中空纤维NaA分子筛膜的表征毕业论文
2020-05-19 21:27:41
摘 要
有机溶剂在石化、食品、医药、环保等领域的广泛应用,反应了有机溶剂在人类生活中的重要性,在我国每年生产和使用的有机溶剂的总量高达亿吨。有机溶剂脱水是有机溶剂在生产和回收使用过程中的关键环节,因此受到工业界的广泛关注。NaA分子筛膜凭借其0.42 nm的有效孔径,对有机溶剂和水起到了很好的筛分作用,以及其孔道内强库伦电场导致的强亲水性,使其在有机溶剂脱水方面表现出良好的水选择性。NaA分子筛膜高通量、高选择性、较好的热化学稳定性,成就了其广阔的应用前景。
现有的技术都是关于在四通道中空纤维的外表面制备NaA分子筛膜,但是内膜(载体内壁成膜)较外膜(载体外壁成膜)更具工业应用前景。因为内膜不仅可以有效的避免膜层在使用和运输的过程中造成机械损伤,而且还能增加在膜组件中的装填密度。虽然内膜有诸多的优点,但是因为其在制备的过程中难以形成均一较薄的晶种层以及合成液的流动方式等困难,所以目前还没有文献报道过在四通道中空纤维内表面制备NaA分子筛膜。
本论文采用内径约为1 mm的四通道中空纤维作为支撑体,对不同的涂晶条件与合成条件下制备的膜进行表征,考察其对膜性能的影响,从而优化涂晶与合成条件以提高膜的通量与选择性。采用真空抽吸法涂覆晶种,综合考察了晶种液流速、晶种液浓度、真空度和涂覆时间对膜性能的影响。最终实验证明,较短的涂晶时间和适中的晶种液流速有利于形成均一较薄的晶种层。在晶种液的流速为500 ml/h、晶种液浓度为1 wt.%、真空度为10 kPa、涂晶时间为5 s的条件下,形成的晶种层,在其上制备出的NaA分子筛内膜表现出较高的分离性能。在75 ˚C下对90 wt.%的乙醇水溶液进行脱水,膜通量达到12.5 kg·m-2·h-1,分离因子达到780。
关键词:NaA分子筛膜 内壁 四通道中空纤维 有机溶剂脱水
Characterization of four-channel hollow fiber NaA zeolite membrane
ABSTRACT
Organic solvents are widely used in the petrochemical, food, medicine, environmental protection and other fields, reflecting the importance of the organic solvent in human life. The total production and use of organic solvents in China each year are almost billion tons. Dehydration of organic solvents is the key process of organic solvents in the production and recycling, so it takes the widespread concern in the industrial production. NaA zeolite membrane by virtue of its effective pore size of 0.42 nm plays a very good role in sieving organic solvent and water , as well as its strong Coulomb field in the channel leading to strong hydrophilic. So these membranes show good dewatering water selectivity in organic solvents. High-throughput, high selectivity and good thermal chemical stability of NaA zeolite membrane leads to the success of its broad application prospects.
Technologies in our knowledge are all about preparing NaA zeolite membrane on the outer surface of four-channel hollow fibers, but the inner-side membrane (the inner wall of the supporter) compared with the outer membrane (the outer wall of the supporter) has more industrial applications. Because the inner-side membrane not only can effectively prevent mechanical damage of the membrane layer caused by use and transport, but also has an increase in the membrane packing density. Although there are many advantages of inner membrane, it is difficult to form a uniform thin seed layer and make the synthetic fluid. So preparing NaA zeolite membrane in the inner surface of four-channel hollow fiber has not yet been reported.
In this dissertation, four-channel hollow fiber which inner diameter is about 1 mm is taken as a supporter. Seed-coated layer prepared under different synthesis conditions are characterized, investigating its impact on membrane performance. By optimizing the synthesis conditions and seed coating conditions, we can improve the flux and selectivity of the membranes. Vacuum aspiration is used to coating seed, giving a comprehensive survey of the flow rate and the concentration of the seed fluid, degree of vacuum and coating times on film properties. Ultimately it proves that shorter time and moderate flow rate of the seed fluid are conducive to the formation of a uniform thin seed layer. The flow rate of the seed fluid is 500 ml/h, the concentration of the seed fluid is 1 wt.%, the degree of vacuum is 10 kPa, the time is under 5 s, the seed layer is formed. On this occasion the NaA zeolite membrane in the inner surface show higher separation performance with a permeation flux of 12.5 kg·m-2·h-1 and separation factor 780 for dehydration of 90 wt.% ethanol/water mixture at 75 ˚C.
Key words: NaA zeolite membrane; inner wall; four-channel hollow fiber; dehydration of organic solvent
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract III
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1引言 1
1.2 传统有机溶剂脱水技术 1
1.2.1 普通精馏 1
1.2.2 特殊精馏 2
1.2.3 吸附技术 3
1.3 渗透汽化技术概述 4
1.3.1 分离原理 5
1.3.2 影响因素 5
1.3.3 渗透汽化膜的性能指标 6
1.3.4 渗透汽化的应用 7
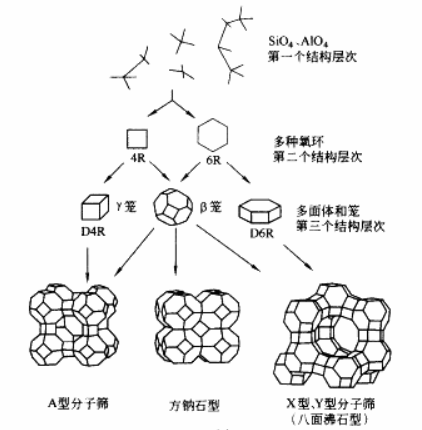
1.4 NaA分子筛膜及其应用 8
1.4.1 概述 8
1.4.2 NaA分子筛膜的合成 10
1.4.3 NaA分子筛膜的应用现状 11
1.5 研究背景和内容 12
第二章 四通道陶瓷中空纤维NaA分子筛内膜的制备与表征 14
2.1 引言 14
2.2 实验内容 14
2.2.1 实验试剂与仪器 14
2.2.2 NaA分子筛膜的制备 15
2.2.3 NaA分子筛膜的表征 16
2.3 结论与讨论 17
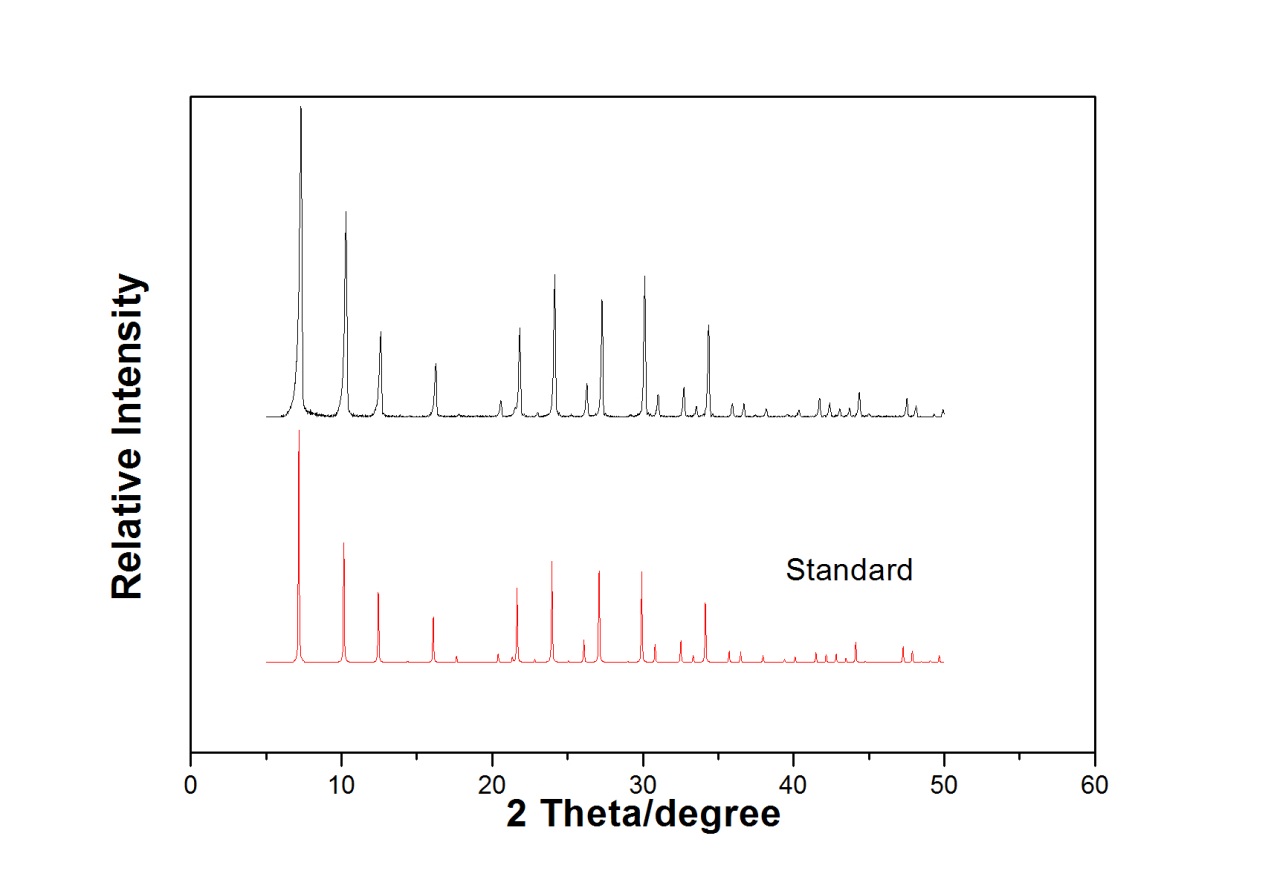
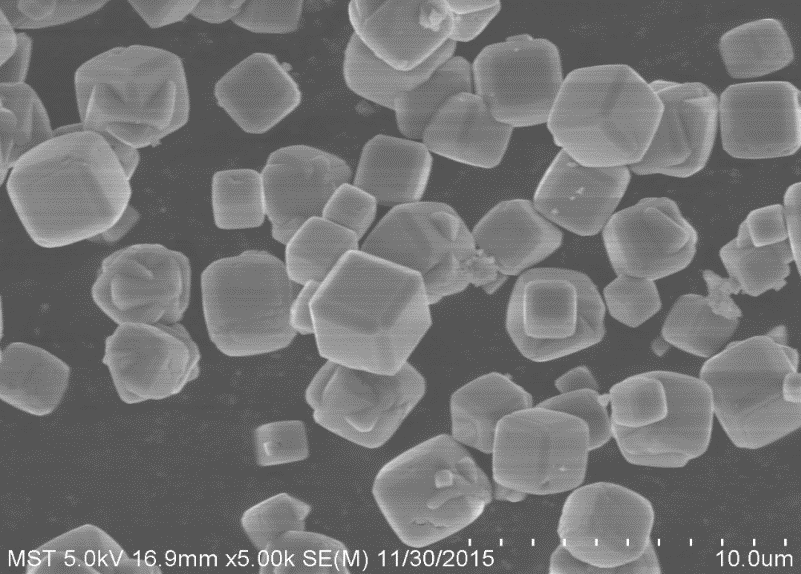
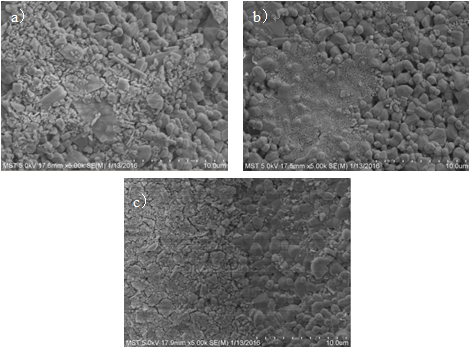
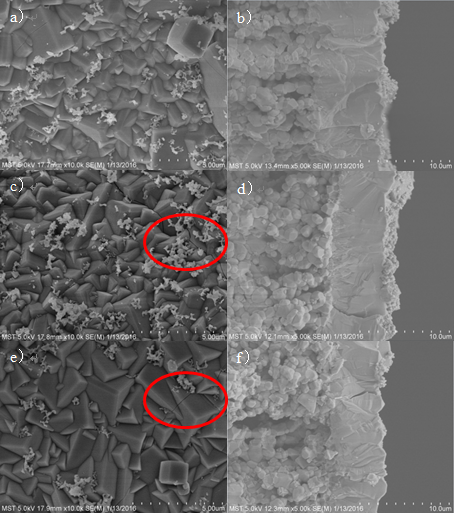
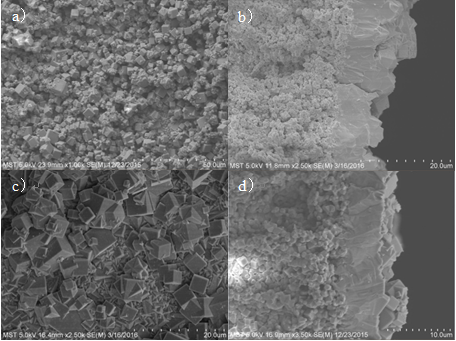
2.3.1 NaA分子筛的表征 17
2.3.2 涂晶时间的影响 18
2.3.3 晶化温度以及晶化时间的影响 19
2.3.4 晶化次数的影响 21
2.3.5 晶种液流速的影响 22
第三章 结论与展望 24
参考文献 25
致谢 27
第一章 文献综述
1.1 引言
膜分离技术是一种高效、节能的新型分离技术,被广泛的应用于石油化工、
医药、食品、环保等方面。在我国每年生产和使用的有机溶剂总量达亿吨。由于有机溶剂在生产和循环的过程中,水是其最主要的杂质,因此实现有机溶剂和水分离过程的节能减排是全球工业界共同关注的焦点问题。目前,我国工业上用于有机溶剂脱水最为普遍的方法还是精馏,精馏是依据两组分相对挥发的不同对其进行分离。由于大多数有机溶剂容易与水形成共沸体系,所以就需要用特殊精馏或吸附等分离方法。但是这些方法能耗高、设备占地面积大、工艺流程复杂而且分离效率低,同时还需要第三组分最为共沸剂、萃取剂或吸附剂,第三组分的加入会对产品和环境都造成污染。因此高效、节能的膜分离技术受到了广泛的关注,成为了实现有机溶剂脱水过程节能减排的重要举措。
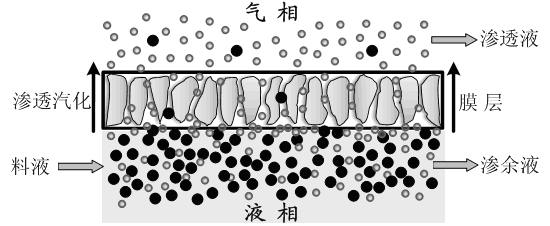
分子筛膜渗透汽化脱水技术,其分离过程简单、不受气液平衡限制、环境友好且能耗低。渗透汽化膜分离技术是依据混合物中各组分在膜中溶解和扩散速率的差异进行分离。因为其分离过程不受热力学平衡的限制,所以适用于共沸体系的分离。目前,用于渗透汽化分离的膜材料主要有有机膜、无机膜以及有机无机杂化膜。与有机膜材料相比,无机膜材料的成本相对较高。但无机膜由于具有良好的热稳定性、化学稳定性和机械稳定性,在渗透汽化领域具有显著优势。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



