电解质阴极界面结构对SOFC电化学性能的影响毕业论文
2020-05-21 22:19:30
摘 要
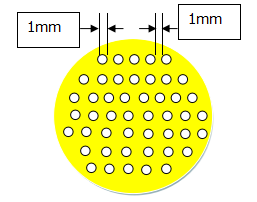
固体氧化物燃料电池(SOFC)的电极阻抗主要来自于阴极极化电阻,而阴极的极化电阻主要与阴极材料以及微观结构有关,因此有规则地改变电解质/阴极界面微观结构能够增加三相反应界面(TPB)的比例,从而增大反应面积,来降低电池阻抗,提高电池阻抗。本实验通过对电解质/阴极表面进行格点状与粗糙面的修饰,来对比各种结构对电池性能的影响。其中,格点状修饰的格点为直径为1mm,间距也为1mm的圆,相对于未修饰的样品,半电池极化电阻减少了3.2%-16.2%,其单电池功率相对于未修饰样品最大增加了45.2%。粗糙表面是用SDC粉料与阴极粘结剂混合的浆料,通过手工刷涂的方式刷在电解质基片上,相比于未修饰的样品,其半电池阻抗增大了35.0%-41.5%。因此,可以得出:有效地改变电解质/阴极界面的结构,增大TPB,便可以降低电极极化阻抗,同时增大单电池电池功率。
关键词:固体氧化物燃料电池 电解质 表面结构 电化学性能
Effect of anode surface mesoscale-structure
on electrochemical properties of SOFC
Abstract
Electrode impedance of solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) is mainly derived from the cathodic polarization resistance.Therefore, a regular change of the microstructure of the electrolyte / cathode interface can increase the ratio of the three phase reaction interface (TPB), thereby increasing the reaction area. Which can reduce the battery impedance and improve the battery impedance.In this experiment, the effects of various structures on the performance of the cell were compared by the modification of the dot array and rough surface of the electrolyte / cathode surface.The dot array modified lattice is a circle which diameter is 1mm, separation distance is 1mm.Related to the unmodified samples, dot array modified samples’ half cell polarization resistance reduced 3.2%-16.2%,and which single battery power related to the unmodified samples, the largest increase rate is 45.2%.Rough surface is mixed by the SDC powder and cathode to binder slurry. Brush the slurry through manual brush on the electrolyte substrate. Compared to unmodified sample, the half cell impedance of rough surface samples increases by 35.0%-41.5%. Therefore, it can be concluded that if the structure of the electrolyte / cathode interface can be effectively changed, the TPB can be increased, the polarization resistance of the electrode can be reduced, and the power of the single battery can be increased simultaneously.
Key Words: solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC); electrolyte; surface structure; electrochemical properties
目 录
摘 要 I
目 录 I
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 SOFC的组成以及工作原理 1
1.3 SOFC的材料 2
1.3.1电解质材料 2
1.3.2阳极材料 3
1.3.3阴极材料 3
1.4 燃料电池极化 3
1.4.1欧姆极化 3
1.4.2浓差极化 3
1.4.3活化极化 4
1.5阴极/电解质界面改性 4
1.6 总结与展望 5
第二章 实验及表征方法 7
2.1 实验原料 7
2.2 实验所需主要设备 7
2.3 实验方法和步骤 8
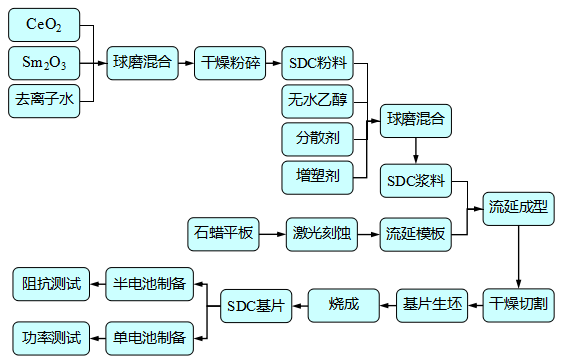
2.3.1实验流程 8
2.3.2 电解质基片表面修饰 9
2.3.3 阴极料浆的制备 10
2.3.4 阳极料浆 10
2.3.5 试样制备 10
2.4. 表征方法 10
2.4.1 阿基米德法测气孔率 10
2.4.2 烧成收缩 11
2.4.3 电化学性能 11
2.4.4 光学显微镜分析 12
2.4.5 扫描电子显微镜分析 13
第三章 结果与讨论 14
3.1 浆料配方的改进 14
3.2 电解质基片气孔率的测定 15
3.3 烧成收缩率 16
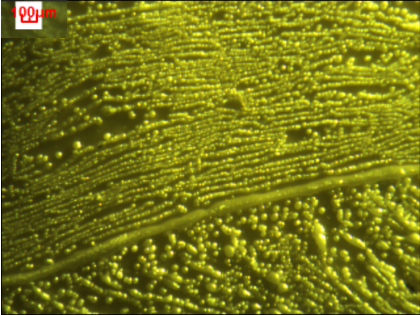
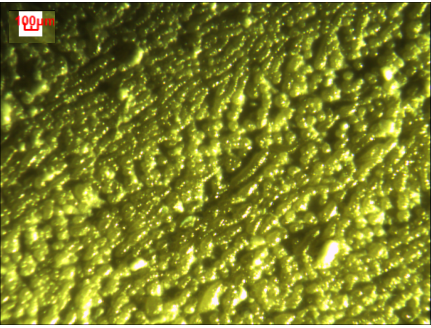
3.4电解质基片的修饰分析 16
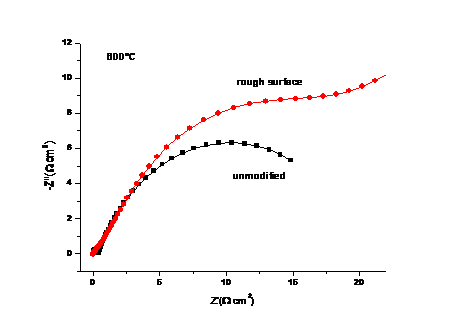
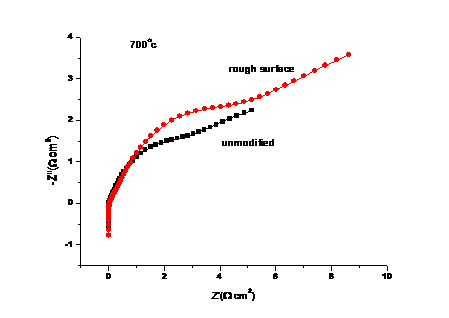
3.5半电池测试 17
3.6单电池测试 22
3.6.1单电池阻抗测试 22
3.6.2 单电池功率测试 24
3.7 电解质/阴极界面结构对SOFC电化学性能的影响分析 25
3.7.1 电解质/阴极界面接触面积的理论计算 25
3.7.2 表面结构对阻抗的影响 26
第四章 结论与展望 28
4.1 结论 28
4.2 展望 28
参考文献 29
致 谢 31
第一章 绪论
1.1 引言
固体氧化物燃料电池( solid oxide fuel cell,SOFC)是通过电化学反应将化学能直接变成电能的一种全固态的发电装置[1],从而避免了使用液态电解质带来的腐蚀和流失等问题;由于SOFC操作温度较高,提高了电化学反应速率,降低了活化极化电势,因此无需使用铂等贵金属作为催化剂;燃料适用性强,除了纯氢作为燃料外,理论上所有能够在阳极被氧化的碳氢化合物,比如甲烷、甲醇等清洁能源都可以作为燃料,所以近年来SOFC被广泛改进利用。
1.2 SOFC的组成以及工作原理
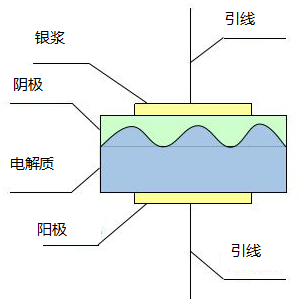
SOFC主要由阴极、阳极和夹在其间的电解质以及连接体组成(如图1-1)。
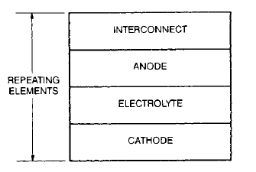
图1-1 固体氧化物燃料电池的基本组成[2]
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



